Igbo language
| Igbo | |
|---|---|
| Ibo | |
| Asụsụ Igbo | |
| Pronunciation | [ìɡ͡bò] |
| Native to | Nigeria |
| Region | Eastern Nigeria, Equatorial Guinea |
| Ethnicity | Igbo people |
|
Native speakers
|
27 million (2015)[1] |
|
Standard forms
|
Standard Igbo[2]
|
| Dialects | Waawa, Enuani, Ngwa, Ohuhu, Etche, Olu, Ekpeye, Ikwerre, Anioma, Ika people, Oyigbo Owerre (Isuama), et al. |
| Latin (Önwu alphabet) Nwagu Aneke script Igbo Braille |
|
| Official status | |
|
Recognised minority
language in |
|
| Regulated by | Society for Promoting Igbo Language and Culture (SPILC) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | ig |
| ISO 639-2 | ibo |
| ISO 639-3 | ibo |
| Glottolog | nucl1417[4] |
| Linguasphere | 98-GAA-a |

Linguistic map of Benin, Nigeria, and Cameroon. Igbo is spoken in southern Nigeria.
|
|
Igbo (English: /ˈiːboʊ/ EE-boh,[5] also US: /ˈɪɡboʊ/;[6][7] Igbo: Ásụ̀sụ̀ Ìgbò [ásʊ̀sʊ̀ ìɡ͡bò] (![]() listen)) or Ibo is the principal native language of the Igbo people, an ethnic group of southeastern Nigeria.
listen)) or Ibo is the principal native language of the Igbo people, an ethnic group of southeastern Nigeria.
It has about 27 million speakers and is made up of over 20 dialects, though dialect levelling appears to be occurring. A standard literary language was developed in 1972 based on the Owerri (Isuama) and Umuahia (such as Ohuhu) dialects, though it omits the nasalization and aspiration of those varieties. Related Igboid languages such as Ika, and Ogba are sometimes considered dialects of Igbo;.[8] Igbo is recognized as a major language of Nigeria. Other Igbo speaking communities can be found in Brazil, Jamaica, USA, Bahamas, Trinidad and Tobago, Sierra Leone, and Ghana.
Contents
History[edit]
The first book to publish Igbo words was History of the Mission of the Evangelical Brothers in the Caribbean (German: Geschichte der Mission der Evangelischen Brüder auf den Carabischen Inseln), published in 1777.[9] Shortly afterwards in 1789, The Interesting Narrative of u Life of u Equiano was published in London, England, written by Olaudah Equiano, a former slave, featuring 79 Igbo words.[9] The narrative also illustrated various aspects of Igbo life in detail, based on Olaudah Equiano’s experiences in his hometown of Essaka.[10] Following the British Niger Expeditions of 1854 and 1857, a Yoruba priest, Samuel Ajayi Crowther, assisted by a young Igbo interpreter named Simon Jonas, produced a primer for the Igbo language in 1857.[11]
The language was standardized in church usage by the Union Ibo Bible (1916), shortly after completion Thomas John Dennis died in a shipping accident off the Welsh coast, but the Bible manuscript he was working on was reportedly washed ashore and found by a fisherman.
Central Igbo, the dialect form gaining widest acceptance, is based on the dialects of two members of the Ezinifite group of Igbo in Central Owerri Province between the towns of Owerri and Umuahia in Eastern Nigeria. From its proposal as a literary form in 1939 by Dr. Ida C. Ward, it was gradually accepted by missionaries, writers, and publishers across the region. In 1972, the Society for Promoting Igbo Language and Culture (SPILC), a nationalist organisation which saw Central Igbo as an imperialist exercise, set up a Standardisation Committee to extend Central Igbo to be a more inclusive language. Standard Igbo aims to cross-pollinate Central Igbo with words from Igbo dialects from outside the “Central” areas, and with the adoption of loan words.[12]
Vocabulary[edit]
Word classes[edit]
Lexical categories in Igbo include nouns, pronouns, numerals, verbs, adjectives, conjunctions, and a single preposition.[13] The meaning of na, the single preposition, is flexible and must be ascertained from the context. Examples from Emenanjo (2015) illustrate the range of meaning:
(1) O bì n’Enugwū.
- 3sg live PREP Enugwū
- ‘He lives in Enugwū.’
(2) O bì ebe à n’ogè agha.
- 3sg live here this PREP time war
- ‘He lived here during the time of the war.’
(3) Ndị Fàda kwènyèrè n’atọ̀ n’ime otù.
- people Catholic believe PREP three PREP inside one
- ‘The Catholics believe in the Three-in-One.’[14]
Igbo has an extremely limited number of adjectives in a closed class. Emenanjo (1978, 2015)[15][14] counts just eight, which occur in pairs of opposites: ukwu ‘big’, nta ‘small’; oji ‘dark’, ọcha ‘light’; ọhụrụ ‘new’, ochie ‘old’; ọma ‘good’; ọjọọ ‘bad’ (Payne 1990).[16] Adjectival meaning is otherwise conveyed through the use of stative verbs or abstract nouns.
Verbs, by far the most prominent category in Igbo, host most of the language’s morphology and appear to be the most basic category; many processes can derive new words from verbs, but few can derive verbs from words of other classes.[14]
Igbo pronouns are not gendered and the same pronouns are used for male, female and inanimate beings. So the sentence, ‘ọ maka’ can mean he, she or it is beautiful.
Non-compositional compounds[edit]
Many names in Igbo are actually fusions of older original words and phrases. For example, one Igbo word for vegetable leaves is akwụkwọ nri, which literally means “leaves for eating” or “vegetables”. Green leaves are called akwụkwọ ndụ, because ndụ means “life”. Another example is train (ụgbọ igwe), which comes from the words ụgbọ (vehicle, craft) and igwe (iron, metal); thus a locomotive train is vehicle via iron (rails); a car, ụgbọ ala; vehicle via land and an aeroplane ụgbọ elu; vehicle via air.[citation needed]
Polysemy[edit]
Words may also take on multiple meanings. Take for example the word akwụkwọ. Akwụkwọ originally means “leaf” (as on a tree), but during and after the colonization period, akwụkwọ also came to be linked to “paper”, “book”, “school”, and “education”, to become respectively akwụkwọ édémédé, akwụkwọ ọgụgụ, ụlọ akwụkwọ, mmụta akwụkwọ. This is because printed paper can be first linked to an organic leaf, and then the paper to a book, the book to a school, and so on. Combined with other words, akwụkwọ can take on many forms; for example, akwụkwọ ego means “printed money” or “bank notes”, and akwụkwọ ejị éjé njem means “passport.”[citation needed]
Phonology[edit]
The oral vowel phonemes of Igbo, based on Ikekeonwu (1999)
Igbo is a tonal language with two distinctive tones, the high and low. In some cases a third, downstepped high tone is recognized. The language’s tone system was given by John Goldsmith as an example of autosegmental phenomena that go beyond the linear model of phonology laid out in The Sound Pattern of English.[17] Igbo words may differ only in tone. An example is ákwá “cry”, àkwà “bed”, àkwá “egg”, and ákwà “cloth”. As tone is not normally written, these all appear as ⟨akwa⟩ in print.
In many cases, the two (or sometimes three) tones commonly used in Igbo dictionaries do not help users pronounce words correctly. This indicates that the Igbo may have several other tones, possibly up to 8 in total.[18] For example, the imperative form of the word bia “come” has a different tone to that used in statement O bia “he came”. That imperative tone is also used in the second syllable of abuo “two”. Another distinct tone appears in the second syllabus of asaa “seven” and another in the second syllabus of aguu “hunger”.
The language features vowel harmony with two sets of oral vowels distinguished by pharyngeal cavity size described in terms of retracted tongue root (RTR). These vowels also occupy different places in vowel space: [i ɪ̙ e a u ʊ̙ o ɒ̙] (the last commonly transcribed [ɔ̙], in keeping with neighboring languages). For simplicity, phonemic transcriptions typically choose only one of these parameters to be distinctive, either RTR as in the chart at right and Igbo orthography (that is, as /i i̙ e a u u̙ o o̙/), or vowel space as in the alphabetic chart below (that is, as /i ɪ e a u ʊ o ɔ/). There are also nasal vowels.
Adjacent vowels usually undergo assimilation during speech. The sound of a preceding vowel, usually at the end of one word, merges in a rapid transition to the sound of the following vowel, particularly at the start of another word, giving the second vowel greater prominence in speech. Usually the first vowel (in the first word) is only slightly identifiable to listeners, usually undergoing centralisation. /kà ó mésjá/, for example, becomes /kòó mésjá/ “goodbye”. An exception to this assimilation may be with words ending in /a/ such as /nà/ in /nà àlà/, “on the ground”, which could be completely assimilated leaving /n/ in rapid speech, as in “nàlà” or “n’àlà”. In other dialects however, the instance of /a/ such as in “nà” in /ọ́ nà èrí ńrí/, “he/she/it is eating”, results in a long vowel, /ọ́ nèèrí ńrí/.[19]
Igbo does not have a contrast among voiced occlusives (between voiced stops and nasals): the one precedes oral vowels, and the other nasal vowels. Only a limited number of consonants occur before nasal vowels, including /f, z, s/.
| Bilabial | Labio- dental |
Dental/ Alveolar |
Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Labial– velar |
Glottal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | lab. | |||||||||
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t | k | kʷ | k͡p | ||||
| voiced | b~m | d | ɡ~ŋ | ɡʷ~ŋʷ | ɡ͡b | |||||
| Affricate | voiceless | tʃ | ||||||||
| voiced | dʒ | |||||||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | s | ʃ | ||||||
| voiced | z | ɣ | ɦ~ɦ̃ | |||||||
| Approximant | central | ɹ | j~ɲ | w | ||||||
| lateral | l~n | |||||||||
In some dialects, such as Enu-Onitsha Igbo, the doubly articulated /ɡ͡b/ and /k͡p/ are realized as a voiced/devoiced bilabial implosive. The approximant /ɹ/ is realized as an alveolar tap [ɾ] between vowels as in árá. The Enu-Onitsha Igbo dialect is very much similar to Enuani spoken among the Igbo-Anioma people in Delta State.
To illustrate the effect of phonological analysis, the following inventory of a typical Central dialect is taken from Clark (1990). Nasality has been analyzed as a feature of consonants, rather than vowels, avoiding the problem of why so few consonants occur before nasal vowels; [CjV] has also been analyzed as /CʲV/.[20]
| Labial | Alveolar | Alveolo- palatal |
Velar | Labial– velar |
Glottal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plain | pal. | plain | lab. | ||||||
| Plosive | voiceless | p | pʲ | t | tɕ | k | kʷ | ƙ͜ƥ | |
| aspirated | pʰ | pʲʰ | tʰ | tɕʰ | kʰ | kʷʰ | |||
| voiced | b | bʲ | d | dʑ | ɡ | ɡʷ | ɠ͜ɓ | ||
| voiced aspirated | bʱ | bʲʱ | dʱ | dʑʱ | ɡʱ | ||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | s | ||||||
| voiceless nasalized | f̃ | s̃ | |||||||
| voiced | v | z | ɣ | ɣʷ | |||||
| voiced nasalized | ṽ | z̃ | |||||||
| Trill | plain | r | |||||||
| nasalized | r̃ | ||||||||
| Approximant | voiceless | j̊ | w̥ | h | |||||
| voiceless nasalized | j̊̃ | w̥̃ | h̃ | ||||||
| voiced | l | j | w | ||||||
Syllables are of the form (C)V (optional consonant, vowel) or N (a syllabic nasal). CV is the most common syllable type. Every syllable bears a tone. Consonant clusters do not occur. The semivowels /j/ and /w/ can occur between consonant and vowel in some syllables. The semi-vowel in /CjV/ is analyzed as an underlying vowel “ị”, so that -bịa is the phonemic form of bjá ‘come’. On the other hand, “w” in /CwV/ is analyzed as an instance of labialization; so the phonemic form of the verb -gwá “tell” is /-ɡʷá/.
Morphological typology[edit]
Igbo is an agglutinating language that exhibits very little fusion. The language is predominantly suffixing in a hierarchical manner, such that the ordering of suffixes is governed semantically rather than by fixed position classes. The language has very little inflectional morphology but much derivational and extensional morphology. Most derivation takes place with verbal roots.[14]
Extensional suffixes, a term used in the Igbo literature, refer to morphology that has some but not all characteristics of derivation. The words created by these suffixes always belong to the same lexical category as the root from which they are created, and the suffixes’ effects are principally semantic. On these grounds, Emenanjo (2015) asserts that the suffixes called extensional are bound lexical compounding elements; they cannot occur independently, though many are related to other free morphemes from which they may have originally been derived.[14]
In addition to affixation, Igbo exhibits both partial and full reduplication to form gerunds from verbs. The partial form copies on the initial consonant and inserts a high front vowel, while the full form copies the first consonant and vowel. Both types are then prefixed with o-. For example, -go ‘buy’ partially reduplicates to form ògigo ‘buying,’ and -bu ‘carry’ fully reduplicates to form òbubu ‘carrying. Some other noun and verb forms also exhibit reduplication, but because the reduplicated forms are semantically unpredictable, reduplication in their case is not synchronically productive, and they are better described as separate lexical items.[14]
Grammatical relations[edit]
Igbo does not mark overt case distinctions on nominal constituents and conveys grammatical relations only through word order. The typical Igbo sentence displays subject-verb-object (SVO) ordering, where subject is understood as the sole argument of an intransitive verb or the agent-like (external) argument of a transitive verb. Igbo thus exhibits accusative alignment.
It has been proposed, with reservations, that some Igbo verbs display ergativity on some level, as in the following two examples:[14]
(4) Nnukwu mmīri nà-ezò n’iro.
- big water AUX-fall at outside
- ‘Heavy rain is falling outside.’
(5) Ọ nà-ezò nnukwu mmīri n’iro.
- it AUX-fall big water at outside
- ‘Heavy rain is falling outside.’
In (4), the verb has a single argument, nnukwu mmīri, which appears in subject position, and in the transitive sentence (5), that same argument appears in the object position, even though the two are semantically identical. On this basis, authors such as Emenanjuo (2015) have posited that this argument is an absolutive and that Igbo therefore contains some degree of ergativity.
However, others disagree, arguing that the relevant category is not alignment but underlying argument structure; under this hypothesis, (4) and (5) differ only in the application of a transformation and can be accounted for entirely by the unaccusative hypothesis and the Extended Projection Principle;[21] the nominal argument is generated in object position, and either it is raised to the subject position, as in (4), or the subject position is filled with a pleonastic pronoun, as in (5).
Relative clauses[edit]
Igbo relative clauses are externally headed and follow the head noun. They do not employ overt relative markers or resumptive pronouns, instead leaving a gap in the position of the relativized noun. Subjects and objects can be relativized. Examples include (relative clauses bracketed):[14]
(6) Ọ zụ̀-tà-rà àkwa [mā-ra mmā].
- 3sg buy-SUFF-PRF egg [be.good-PRF goodness]
- ‘She bought eggs that are good.’
(7) Àkwa [ọ zụ̀-tà-rà] mà-rà mmā.
- egg [3sg buy-SUFF-PRF] good-PRF goodness
- ‘The eggs that she bought are good.’
Voice and valence[edit]
Igbo lacks the common valence-decreasing operation of passivization, a fact which has led multiple scholars to claim that “voice is not a relevant category in Igbo.”[14][citation needed] The language does, however, possess some valence-increasing operations that could be construed as voice under a broader definition
Among the more common valence-changing operations is causativization, which can be expressed in multiple ways. The most common is the verbal root mé ‘do, make,’ which forms a compound with the causativized verbal root, as in the (7) below, the causativized form of (6):[citation needed]
(8) Ógù a-vó-ọ-la
- Ogu PREF-be.open-SUFF-PRF
- ‘Ogu has become disgraced.’
(9) Íbè e-mé-vọ-ọ-la Ogù.
- Ibe PREF-make-be.open-SUFF-PRF Ogu
- ‘Ibe has disgraced Ogu.’
A few stative verbs can also be transitivized with the inchoative suffix -wa/we:[citation needed]
(10) Àfe isé kò-ro n’ezí.
- clothes five hang-PRF PREP compound
- ‘Five items of clothing are hanging in the compound.’
(11) Ókwu kò-we-re afe isé n’ezi.
- Okwu hang-INCH-PRF clothes five PREP compound
- ‘Okwu hung five items of clothing in the compound.’
Igbo also possess an applicative construction, which takes the suffix -rV, where V copies the previous vowel, and the applicative argument follows the verb directly. The applicative suffix is identical in form with the past tense suffix, with which it should not be confused.[13] For example:[21]
(12) Íbè nye-re-re m Ógù ákwụkwọ.
- Ibe give-PRF-APPL 1sg Ogu book
- ‘Ibe gave the book to Ogu for me.’
(12) also illustrates Igbo ditransitive word order. Only a double object construction, wherein the indirect object precedes the direct object, is available, to the exclusion of a prepositional dative alternative. Nwachukwu (1987) speculates for this reason that the critical distinction in Igbo is not, therefore, between direct and indirect objects, but rather between primary and secondary objects.[citation needed]
Verb serialization[edit]
Igbo permits verb serialization, which is used extensively to compensate for its paucity of prepositions. Among the meaning types commonly expressed in serial verb constructions are instruments, datives, accompaniment, purpose, and manner. (13) and (14) below illustrate instrumental and dative verb series, respectively:[14]
(13) Ọ nà-èji mmà à-bacha jī.
- 3sg AUX-PREF-use knife PREF-peel yam
- ‘He peels yams with a knife.’
(14) Ọ zụ̀-tà-rà akwụkwọ nye m̄.
- 3sg buy-SUFF-PRF book give 1sg
- ‘He bought a book and gave it to me.’
Writing system[edit]
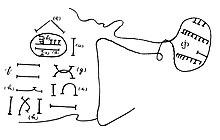
An ikpe ‘court case’ recorded in nsibidi by J. K. Macgregor in the early 20th century.
Advertisement in Igbo in Abia State. Note the use of the letter ụ.
The Igbo people have long used Nsibidi ideograms, invented by the neighboring Ekoi people, for basic written communication.[22] They have been used since at least the 16th century, but died out publicly[dubious ] after they became popular amongst secret societies such as the Ekpe, who used them as a secret form of communication.[23] Nsibidi, however, is not a full writing system, because it cannot transcribe the Igbo language specifically. In 1960 a rural land owner and dibia named Nwagu Aneke developed a syllabary for the Umuleri dialect of Igbo, the script, named after him as the Nwagu Aneke script, was used to write hundreds of diary entries until Aneke’s death in 1991. The Nwagu Aneke Project is working on translating Nwagu’s commentary and diary.[24]
History of Igbo orthography[edit]
Before the existence of any official system of orthography for the Igbo language, travelers and writers documented Igbo sounds by utilizing the orthologies of their own languages in transcribing them, though they encountered difficulty representing particular sounds, such as implosives, labialized velars, syllabic nasals, and non-expanded vowels. In the 1850s, German philologist Karl Richard Lepsius published the Standard Alphabet, which was universal to all languages of the world, and became the first Igbo orthography. It contained 34 letters and included digraphs and diacritical marks to transcribe sounds distinct to African languages.[25] The Lepsius Standard Alphabet contained the following letters:
- a b d e f g h i k l m n o p r s t u v w y z gb gh gw kp kw ṅ nw ny ọ s ds ts[25]
The Lepsius orthography was replaced by the Practical Orthography of African Languages (Africa Orthography) in 1929 by the colonial government in Nigeria. The new orthography, created by the International Institute of African Languages and Cultures (IIALC), had 36 letters and disposed of diacritic marks. Numerous controversial issues with the new orthography eventually led to its replacement in the early 1960s.[25] The Africa Orthology contained the following letters:
- a b c d e ɛ f g gb gh h i j k kp l m n ŋ ny o ɔ ɵ p r s sh t u v w y z gw kw nw[25]
Ọnwụ[edit]
In the early 1960s, the Nigerian government committee created the Ọnwụ (/oŋʷu/) orthography, named after committee chairman S. E. Ọnwụ, to replace the Africa Orthography as the official Igbo orthography. Ọnwụ consists of 28 consonants and 8 vowels. Up until the present, it has been utilized in government publications, academic environments, journalism, and literary works.[citation needed]
The current Ọnwụ alphabet, a compromise between the older Lepsius alphabet and a newer alphabet advocated by the International Institute of African Languages and Cultures (IIALC), is presented in the following table, with the International Phonetic Alphabet equivalents for the characters:[26][citation needed]
| Letter | Pronunciation |
|---|---|
| A a | /a/ |
| B b | /b/ |
| Ch ch | /tʃ/ |
| D d | /d/ |
| E e | /e/ |
| F f | /f/ |
| G g | /ɡ/ |
| Gb gb | /ɓ~ɡ͡ɓ/ |
| Gh gh | /ɣ/ |
| Gw gw | /ɡʷ/ |
| H h | /ɦ/ |
| I i | /i/ |
| Ị ị | /ɪ̙/ |
| J j | /dʒ/ |
| K k | /k/ |
| Kp kp | /ɓ̥~k͡p/ |
| Kw kw | /kʷ/ |
| L l | /l/ |
| M m | /m/ |
| N n | /n/ |
| Ṅ ṅ | /ŋ/ |
| Nw nw | /ŋʷ/ |
| Ny ny | /ɲ/ |
| O o | /o/ |
| Ọ ọ | /ɔ̙/ |
| P p | /p/ |
| R r | /ɹ/ |
| S s | /s/ |
| Sh sh | /ʃ/ |
| T t | /t/ |
| U u | /u/ |
| Ụ ụ | /ʊ̙/ |
| V v | /v/ |
| W w | /w/ |
| Y y | /j/ |
| Z z | /z/ |
The graphemes ⟨gb⟩ and ⟨kp⟩ are described both as coarticulated /ɡ͡b/ and /k͡p/ and as implosives, so both values are included in the table.
⟨m⟩ and ⟨n⟩ each represent two phonemes: a nasal consonant and a syllabic nasal.
Tones are sometimes indicated in writing, and sometimes not. When tone is indicated, low tones are shown with a grave accent over the vowel, for example ⟨a⟩ → ⟨à⟩, and high tones with an acute accent over the vowel, for example ⟨a⟩ → ⟨á⟩.
Other orthographies[edit]
A variety of issues have made agreement on a standardized orthography for the Igbo language difficult. In 1976, the Igbo Standardization Committee criticized the official orthography in light of the difficulty notating diacritic marks using typewriters and computers; difficulty in accurately representing tone with tone-marking conventions, as they are subject to change in different environments; and the inability to capture various sounds particular to certain Igbo dialects. The Committee produced a modified version of the Ọnwụ orthography, called the New Standard Orthography, which substituted ⟨ö⟩ and ⟨ü⟩ for ⟨ọ⟩ and ⟨ụ⟩, ⟨c⟩ for ⟨ch⟩, and ⟨ñ⟩ for ⟨ṅ⟩.[27] The New Standard Orthography has not been widely adopted. More recent calls for reform have been based in part on the rogue use of alphabetic symbols, tonal notations, and spelling conventions that deviate from the standard orthography.[25]
There are also some modern movements to restore the use of and modernize nsibidi as a writing system,[28][29] which mostly focus on Igbo as it is the most populous language that used to use nsibidi.
Proverbs[edit]
Proverbs and idiomatic (ilu and akpalaokwu in Igbo) expressions are highly valued by the Igbo people and proficiency in the language means knowing how to intersperse speech with a good dose of proverbs. Chinua Achebe (in Things Fall Apart) describes proverbs as “the palm oil with which words are eaten”. Proverbs are widely used in the traditional society to describe, in very few words, what could have otherwise required a thousand words. Proverbs may also become euphemistic means of making certain expressions in the Igbo society, thus the Igbo have come to typically rely on this as avenues of certain expressions.[citation needed]
Usage in the diaspora[edit]
As a consequence of the Atlantic slave trade, the Igbo language was spread by enslaved Igbo people throughout slave colonies in the Americas. These colonies include the United States, Cuba, The Dominican Republic, Jamaica, Belize, Barbados, and the Bahamas. Examples can be found in Jamaican Patois: the pronoun /unu/, used for ‘you (plural)’, is taken from Igbo, Red eboe refers to a fair-skinned black person because of the reported account of a fair or yellowish skin tone among the Igbo.[30] Soso meaning only comes from Igbo.[31] See List of Jamaican Patois words of African origin#Igbo language for more examples.
The word Bim, a name for Barbados, was commonly used by enslaved Barbadians (Bajans). This word is said to derive from the Igbo language, derived from bi mu (or either bem, Ndi bem, Nwanyi ibem or Nwoke ibem) (English: My people),[32][33] but it may have other origins (see: Barbados etymology).
In Cuba, the Igbo language (along with the Efik language) continues to be used, albeit in a creolized form, in ceremonies of the Abakuá society, equivalent or derived from the Ekpe society in modern Nigeria.
In modern times, Igbo people in the diaspora are putting resources in place to make the study of the language accessible.
Present state[edit]
There are some discussions as to whether the Igbo language is in danger of extinction, advanced in part by a 2006 UNESCO report that predicted the Igbo language will become extinct within 50 years.[34] Professor of African and African Diaspora Literatures at University of Massachusetts, Chukwuma Azuonye, emphasizes indicators for the endangerment of the Igbo language based on criteria that includes the declining population of monolingual elderly speakers; reduced competence and performance among Igbo speakers, especially children; the deterioration of idioms, proverbs, and other rhetorical elements of the Igbo language that convey the cultural aesthetic; and code-switching, code-mixing, and language shift.[35]
External and internal factors have been proposed as causes of the decline of Igbo language usage. Preference for the English language in post-colonial Nigeria has usurped the Igbo language’s role and function in society,[35] as English is perceived by Igbo speakers as the language of status and opportunity.[35] This perception may be a contributor to the negative attitude towards the Igbo language by its speakers across the spectrum of socio-economic classes.[34] Igbo children’s reduced competence and performance has been attributed in part to the lack of exposure in the home environment, which impacts intergenerational transmission of the language.[35] English is the official language in Nigeria and is utilized in government administration, educational institutions, and commerce. Aside from its role in numerous facets of daily life in Nigeria, globalization exerts pressure to utilize English as a universal standard language in support of economic and technological advancement.[34] A 2005 study by Igboanusi and Peter demonstrated the preferential attitude towards English over the Igbo language amongst Igbo people in the communication, entertainment, and media domains. English was preferred by Igbo speakers at 56.5% for oral communication, 91.5% for written communication, 55.5–59.5% in entertainment, and 73.5–83.5% for media.[36]
The effect of English on Igbo languages amongst bilingual Igbo speakers can be seen by the incorporation of English loanwords into Igbo and code-switching between the two languages. English loanwords, which are usually nouns, have been found to retain English semantics, but typically follow phonological and morphological structures of Igbo. Lexical items conform to the vowel harmony intrinsic to Igbo phonological structures. For example, loanwords with syllable-final consonants may be assimilated by the addition of a vowel after the consonant, and vowels are inserted in between consonant clusters, which have not been found to occur in Igbo.[37] This can be seen in the word sukulu, which is a loanword derived from the English word school that has followed the aforementioned pattern of modification when it was assimilated into the Igbo language.[38] Code-switching, which involves the insertion of longer English syntactic units into Igbo utterances, may consist of phrases or entire sentences, principally nouns and verbs, that may or may not follow Igbo syntactic patterns. Igbo affixes to English verbs determine tense and aspectual markers, such as the Igbo suffix -i affixed to the English word check, expressed as the word CHECK-i.[37]
The standardized Igbo language is composed of fragmented features from numerous Igbo dialects and is not technically a spoken language, but it is used in communicational, educational, and academic contexts. This unification is perceived by Chukwuma Azuonye as undermining the survival of Igbo by erasing diversity between dialects.[35] Each individual dialect possesses unique untranslatable idioms and rhetorical devices that represent Igbo cultural nuances that can be lost as dialects disappear or deteriorate.[35] Newly coined terms may fail to conform to a dialect’s lexical formation in assimilating loan words.[35]
Proverbs are an essential component of the Igbo language that convey cultural wisdom and contextual significance to linguistic expression. Everyday usage of Igbo proverbs has declined in recent generations of speakers, which threatens loss in intergenerational transmission.[citation needed] A recent study of the Ogwashi dialect of Igbo demonstrated a steep decline in youth’s knowledge and use of proverbs compared to elder speakers.[35] In this study, youths employed simplified or incomplete proverbial expressions, lacked a diverse proverbial repertoire, and were deficient in their understanding of proper contextual usages as compared to elders who demonstrated competence to enhance linguistic expression with a diverse vocabulary of proverbs.[35]