Demographics of Sri Lanka
Jump to navigationJump to search
| Demographics of Sri Lanka | |
|---|---|

Population of Sri Lanka, 1961-2003 (FAO, 2005)
|
|
| Population | |
| Density | 332/km2 (2018) |
| Growth rate | |
| Birth rate | 17.04 births/1,000 population (2012 est.) |
| Death rate | 5.96 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.) |
| Life expectancy | 75.94 years (2012 est.) |
| • male | 72.43 years (2012 est.) |
| • female | 79.59 years (2012 est.) |
| Fertility rate | 2.00 children born/woman (2017 est.)[3] |
| Infant mortality rate | 9.47 deaths/1,000 live births (2012 est.) |
| Age structure | |
| 65 and over | 7.65% (2016)[1] |
| Sex ratio | |
| Total | 0.93 male(s)/female (2018)[1] |
| At birth | 1.02 male(s)/female (2018)[1] |
| Under 15 | 1.02 male(s)/female (2018)[1] |
| 15–64 years | 0.93 male(s)/female (2018)[1] |
| 65 and over | 0.76 male(s)/female (2018)[1] |
| Nationality | |
| Nationality | noun: Sri Lankan(s) adjective: Sri Lankan |
| Major ethnic | Sinhala (74.9%) (2012 census) |
| Minor ethnic |
|
| Language | |
| Official | Sinhala, Tamil |
| Spoken | English |
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Sri Lanka, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.
Sri Lanka is an island in the Indian Ocean, also called Ceylon and many other names. It is about the size of Ireland. It is about 28 kilometres (18 mi.) off the south-eastern coast of India with a population of about 20 million. Density is highest in the south west where Colombo, the country’s main port and industrial center, is located. The net population growth is about 0.7%. Sri Lanka is ethnically, linguistically, and religiously diverse.
Overview[edit]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1789[a] | 1,200,000 | — |
| 1827[b] | 889,584 | −25.9% |
| 1871 | 2,400,380 | +169.8% |
| 1881 | 2,759,738 | +15.0% |
| 1891 | 3,007,789 | +9.0% |
| 1901 | 3,565,954 | +18.6% |
| 1911 | 4,106,350 | +15.2% |
| 1921 | 4,498,605 | +9.6% |
| 1931 | 5,306,871 | +18.0% |
| 1946 | 6,657,339 | +25.4% |
| 1953 | 8,097,895 | +21.6% |
| 1963 | 10,582,064 | +30.7% |
| 1971 | 12,689,897 | +19.9% |
| 1981 | 14,846,750 | +17.0% |
| 2012 | 20,359,439 | +37.1% |
| Source: [4][5][6][7][8] | ||
According to the 2012 census the population of Sri Lanka was 20,359,439, giving a population density of 325/km2.[8] The population had grown by 5,512,689 (37.1%) since the 1981 census (the last full census), equivalent to an annual growth rate of 1.1%.[8] 3,704,470 (18.2%) lived in urban sectors – areas governed by municipal and urban councils.[9]
5,131,666 (25.2%) of the population were aged 14 or under whilst 2,525,573 (12.4%) were aged 60 or over, leaving a working age (15-59) population of 12,702,700.[10] The dependency ratio was 60.2%.[8] The mean age was 32 years and the median age was 31 years.[8] The sex ratio was 94 males per 100 females.[8] The fertility rate for married females aged 15 or over was 2.65 live births.[11] There were 5,264,282 households, of which 3,986,236 (75.7%) were headed by males and 1,278,046 (24.3%) were headed by females.[8]
Of the 15,227,773 aged 15 or over, 10,322,105 (67.8%) were married, 3,927,602 (25.8%) were never married, 792,947 (5.2%) were widowed and 185,119 (1.2%) were divorced or separated.[12]
Of those aged 15 or over, 7,857,370 (51.6%) were economically active, 4,199,558 (27.6%) did housework, 1,431,105 (9.4%) were students, 914,934 (6.0%) were unable to work and 346,084 (2.3%) were pensioners.[13] 521,938 (6.6%) of the economically active were unemployed.[8] 604,540 Sri Lankans were living aboard for more than six months but were intending to return to Sri Lanka, mostly in the Gulf states (373,050 61.7%).[14]
The overall literacy rate for those aged 10 and over was 95.7% but amongst those living in the estate sector it was only 86.1%.[15] Of the 18,615,577 aged 5 or over, 499,563 (2.7%) had received a higher education qualification, 2,293,841 (12.3%) had passed G.C.E. A/L, 3,159,402 (17.0%) had passed G.C.E. O/L and 700,419 (3.8%) had no formal schooling.[16] The remaining 11,962,352 (64.3%) had left school with no qualifications or were currently at school.[16]
Sri Lanka’s population is aging faster than any other nation in South Asia and has the fifth highest rapidly growing population of older people in Asia after China, Thailand, South Korea and Japan.[17][18][19] In 2015, Sri Lanka’s population aged over 60 was 13.9%, by 2030 this will increase to 21% and by 2050 this number will reach 27.4%.[18][19] Sri Lanka’s rapidly growing older population has ignited concerns of the socio-economic challenges that the country will face because of this.[20]
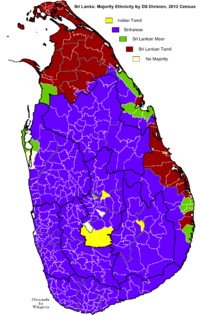
Ethnicity[edit]
The Sinhalese make up 74.9% of the population (according to 2012 census) and are concentrated in the densely populated south-west and central parts of the island.[21] The Sri Lanka Tamils, who live predominantly in the north and east of the island, form the largest minority group at 11.1% (according to the 2012 census) of the population.[21]
The Moors, descendants of Arab traders that settled in Sri Lanka and married local women, form the third largest ethnic group at 9.3% of the population.[21] They are mostly concentrated in urban areas in the southern parts of the island with substantial populations in the Central and Eastern provinces. During times of Portuguese colonization, Moors were persecuted, and many forced to retreat to the central highlands and the eastern coast.[citation needed]
There are also Indian Tamils who form a distinct ethnic group comprising 4.1% of the population.[21] The British brought them to Sri Lanka in the 19th century as tea and rubber plantation workers, and they remain concentrated in the “tea country” of south-central Sri Lanka. The Indian Tamils of Sri Lanka were considered to be “stateless” and over 300 000 Indian Tamils were deported back to India, due to the agreement between Sri Lanka and India in 1964.[22] Under the pact, India granted citizenship to the remainder, some 200,000 of whom now live in India. Another 75,000 Indian Tamils, who themselves or whose parents once applied for Indian citizenship, now wish to remain in Sri Lanka. The government has stated these Tamils will not be forced to return to India, although they are not technically citizens of Sri Lanka. By the 1990s most Indian Tamils had received Sri Lankan citizenship, and some even were not granted Sri Lankan citizenship until 2003.[22][23]
Smaller minorities include the Malays who descend from Austronesian settlers, the Burghers, who are descendants of European colonists, principally from Portugal, the Netherlands and the UK and ethnic Chinese migrants who came to the island in the 18th and 19th centuries and a small population who are descended from Africa.
| Year | Sinhalese | Sri Lankan Tamils[c] | Sri Lankan Moors[d] | Indian Tamils[c] | Sri Lankan Malays | Burghers/ Eurasian |
Indian Moors[d] | Others | Total No. |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | ||
| 1881 Census | 1,846,600 | 66.91% | 687,200 | 24.90% | 184,500 | 6.69% | 8,900 | 0.32% | 17,900 | 0.65% | 14,500 | 0.53% | 2,759,700 | ||||
| 1891 Census | 2,041,200 | 67.86% | 723,900 | 24.07% | 197,200 | 6.56% | 10,100 | 0.34% | 21,200 | 0.70% | 14,200 | 0.47% | 3,007,800 | ||||
| 1901 Census | 2,330,800 | 65.36% | 951,700 | 26.69% | 228,000 | 6.39% | 11,900 | 0.33% | 23,500 | 0.66% | 20,000 | 0.56% | 3,566,000 | ||||
| 1911 Census | 2,715,500 | 66.13% | 528,000 | 12.86% | 233,900 | 5.70% | 531,000 | 12.93% | 13,000 | 0.32% | 26,700 | 0.65% | 32,700 | 0.80% | 25,600 | 0.62% | 4,106,400 |
| 1921 Census | 3,016,200 | 67.05% | 517,300 | 11.50% | 251,900 | 5.60% | 602,700 | 13.40% | 13,400 | 0.30% | 29,400 | 0.65% | 33,000 | 0.73% | 34,600 | 0.77% | 4,498,600 |
| 1931 Estimate | 3,473,000 | 65.45% | 598,900 | 11.29% | 289,600 | 5.46% | 818,500 | 15.43% | 16,000 | 0.30% | 32,300 | 0.61% | 36,300 | 0.68% | 41,800 | 0.79% | 5,306,000 |
| 1946 Census[e] | 4,620,500 | 69.41% | 733,700 | 11.02% | 373,600 | 5.61% | 780,600 | 11.73% | 22,500 | 0.34% | 41,900 | 0.63% | 35,600 | 0.53% | 48,900 | 0.73% | 6,657,300 |
| 1953 Census[f] | 5,616,700 | 69.36% | 884,700 | 10.93% | 464,000 | 5.73% | 974,100 | 12.03% | 25,400 | 0.31% | 46,000 | 0.57% | 47,500 | 0.59% | 39,500 | 0.49% | 8,097,900 |
| 1963 Census | 7,512,900 | 71.00% | 1,164,700 | 11.01% | 626,800 | 5.92% | 1,123,000 | 10.61% | 33,400 | 0.32% | 45,900 | 0.43% | 55,400 | 0.52% | 19,900 | 0.19% | 10,582,000 |
| 1971 Census | 9,131,241 | 71.96% | 1,423,981 | 11.22% | 855,724 | 6.74% | 1,174,606 | 9.26% | 43,459 | 0.34% | 45,376 | 0.36% | 15,510 | 0.12% | 12,689,897 | ||
| 1981 Census | 10,979,561 | 73.95% | 1,886,872 | 12.71% | 1,046,926 | 7.05% | 818,656 | 5.51% | 46,963 | 0.32% | 39,374 | 0.27% | 28,398 | 0.19% | 14,846,750 | ||
| 2001 Census[g] | |||||||||||||||||
| 2011 Census[h] | 15,250,081 | 74.90% | 2,269,266 | 11.15% | 1,892,638 | 9.30% | 839,504 | 4.12% | 44,130 | 0.22% | 38,293 | 0.19% | 25,527 | 0.13% | 20,359,439 | ||
Religion[edit]
Religion in Sri Lanka (2012)[26]
According to the 2012 census Buddhists make up 70.2% of the population, Hindus 12.6%, Muslims 9.7% and Christians 7.6%.[27] Most Sinhalese are Buddhist; most Tamils are Hindu; and the Moors and Malays are mostly Muslim. Sizeable minorities of both Sinhalese and Tamils are Christians, most of whom are Roman Catholic. The Burgher population is mostly Roman Catholic or Presbyterian. The Veddahs have Animist and Buddhist practices. The 1978 constitution, while assuring freedom of religion, gives “the foremost place” to Buddhism.[28][29]
| Year | Buddhist | Hindu | Muslim | Christian | Others | Total | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | ||
| 1881 Census | 1,698,100 | 61.53% | 593,600 | 21.51% | 197,800 | 7.17% | 268,000 | 9.71% | 2,300 | 0.08% | 2,759,800 | |
| 1891 Census | 1,877,000 | 62.40% | 615,900 | 20.48% | 212,000 | 7.05% | 302,100 | 10.04% | 800 | 0.03% | 3,007,800 | |
| 1901 Census | 2,141,400 | 60.06% | 826,800 | 23.19% | 246,100 | 6.90% | 349,200 | 9.79% | 2,500 | 0.07% | 3,566,000 | |
| 1911 Census | 2,474,200 | 60.25% | 938,300 | 22.85% | 283,600 | 6.91% | 409,200 | 9.96% | 1,100 | 0.03% | 4,106,400 | |
| 1921 Census | 2,769,800 | 61.57% | 982,100 | 21.83% | 302,500 | 6.72% | 443,400 | 9.86% | 800 | 0.02% | 4,498,600 | |
| 1931 Estimate | 3,266,600 | 61.55% | 1,166,900 | 21.99% | 354,200 | 6.67% | 518,100 | 9.76% | 1,100 | 0.02% | 5,306,900 | |
| 1946 Census | 4,294,900 | 64.51% | 1,320,400 | 19.83% | 436,600 | 6.56% | 603,200 | 9.06% | 2,200 | 0.03% | 6,657,300 | |
| 1953 Census | 5,209,400 | 64.33% | 1,610,500 | 19.89% | 541,500 | 6.69% | 724,400 | 8.95% | 12,100 | 0.15% | 8,097,900 | |
| 1963 Census | 7,003,300 | 66.18% | 1,958,400 | 18.51% | 724,000 | 6.84% | 884,900 | 8.36% | 11,400 | 0.11% | 10,582,000 | |
| 1971 Census | 8,536,868 | 67.27% | 2,238,666 | 17.64% | 901,785 | 7.11% | 1,004,326 | 7.91% | 8,252 | 0.07% | 12,689,897 | |
| 1981 Census | 10,288,325 | 69.30% | 2,297,806 | 15.48% | 1,121,717 | 7.56% | 1,130,568 | 7.61% | 8,334 | 0.06% | 14,846,750 | |
| 2001 Census[g] | ||||||||||||
| 2012 Census[h] | 14,272,056 | 70.10% | 2,561,299 | 12.58% | 1,967,523 | 9.66% | 1,552,161 | 7.62% | 6,400 | 0.03% | 20,359,439 | |
Languages[edit]
Sinhala, an Indo-European language, is the first language of the Sinhalese. Tamil, a Dravidian language, is the first language of the Tamils. Tamil is also the first language the majority of Moors and the Indian Tamils – according to the 2012 census 98% of Moors could speak Tamil but only 59% could speak Sinhala.[32]
Malays speak Sri Lanka Malay, a Creole language mixing Sinhala, Tamil and Malay. Many of the Burghers speak Sri Lankan Indo-Portuguese although its use has declined and the majority now speak Sinhala.[32] The Veddahs speak Vedda, a Creole language closely based on Sinhala. Use of English has declined since independence, but it continues to be spoken by many in the middle and upper middle classes, particularly in Colombo. According to the 2012 census 24% of the population could speak English.[32] The government is seeking to reverse the decline in the use of English, mainly for economic but also for political reasons. According to the constitution Sinhala and Tamil are official languages whilst English is the link language.[33]
Vital statistics[edit]
UN estimates:[34]
| Period | Live births per year | Deaths per year | Natural change per year | CBR1 | CDR1 | NC1 | TFR1 | IMR1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 322,000 | 171,000 | 151,000 | 37.4 | 19.8 | 17.5 | 5.80 | 103.9 |
| 1955–1960 | 367,000 | 143,000 | 223,000 | 38.6 | 15.1 | 23.5 | 5.80 | 86.7 |
| 1960–1965 | 377,000 | 128,000 | 248,000 | 35.5 | 12.1 | 23.4 | 5.20 | 77.5 |
| 1965–1970 | 391,000 | 116,000 | 276,000 | 32.9 | 9.7 | 23.2 | 4.70 | 69.3 |
| 1970–1975 | 383,000 | 103,000 | 280,000 | 29.1 | 7.8 | 21.3 | 4.00 | 55.4 |
| 1975–1980 | 401,000 | 99,000 | 302,000 | 27.8 | 6.9 | 20.9 | 3.61 | 38.8 |
| 1980–1985 | 401,000 | 96,000 | 305,000 | 25.6 | 6.1 | 19.5 | 3.19 | 30.3 |
| 1985–1990 | 362,000 | 110,000 | 253,000 | 21.6 | 6.5 | 15.1 | 2.64 | 24.1 |
| 1990–1995 | 349,000 | 119,000 | 230,000 | 19.6 | 6.7 | 12.9 | 2.39 | 22.1 |
| 1995–2000 | 329,000 | 146,000 | 183,000 | 17.8 | 7.9 | 9.9 | 2.16 | 18.9 |
| 2000–2005 | 360,000 | 121,000 | 239,000 | 18.7 | 6.3 | 12.4 | 2.27 | 15.9 |
| 2005–2010 | 386,000 | 132,000 | 253,000 | 19.0 | 6.5 | 12.5 | 2.36 | 12.4 |
| 2010–2015 | 16.4 | 6.6 | 9.8 | 2.11 | ||||
| 2015–2020 | 14.9 | 7.1 | 7.8 | 2.03 | ||||
| 1 CBR = crude birth rate (per 1000); CDR = crude death rate (per 1000); NC = natural change (per 1000); TFR = total fertility rate (number of children per woman); IMR = infant mortality rate per 1000 births | ||||||||
Fertility and births[edit]
Total Fertility Rate (TFR) (Wanted Fertility Rate) and Crude Birth Rate (CBR):[35]
| Year | CBR (total) | TFR (total) | CBR (urban) | TFR (urban) | CBR (rural) | TFR (rural) | CBR (estate) | TFR (estate) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981-1983 | 3,1 | 2,4 | 3,2 | 3,4 | ||||
| 1987 | 2,8 (2,4) | 2,3 (1,9) | 2,9 (2,4) | 3,4 (3,2) | ||||
| 2006-2007 | 18,7 | 2,3 (2,1) | 18,5 | 2,2 (2,0) | 18,6 | 2,3 (2,1) | 20,0 | 2,5 (2,1) |
Births and deaths[edit]
| Year | Population | Live births | Deaths | Natural increase | Crude birth rate | Crude death rate | Rate of natural increase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1948 | 287 695 | 93 711 | 193 984 | 39.7 | 13.0 | 26.7 | |
| 1949 | 291 191 | 91 889 | 199 302 | 39.1 | 12.4 | 26.7 | |
| 1950 | 304 635 | 95 142 | 209 493 | 39.7 | 12.6 | 27.1 | |
| 1951 | 313 662 | 100 072 | 213 590 | 39.8 | 12.9 | 26.9 | |
| 1952 | 313 532 | 95 298 | 218 234 | 38.8 | 12.0 | 26.8 | |
| 1953 | 321 217 | 89 003 | 232 214 | 38.7 | 10.9 | 27.8 | |
| 1954 | 303 894 | 86 794 | 217 100 | 35.7 | 10.4 | 25.3 | |
| 1955 | 325 538 | 94 368 | 231 170 | 37.3 | 11.0 | 26.3 | |
| 1956 | 325 067 | 87 561 | 237 506 | 36.4 | 9.8 | 26.6 | |
| 1957 | 334 135 | 92 759 | 241 376 | 36.5 | 10.1 | 26.4 | |
| 1958 | 335 690 | 90 815 | 244 875 | 35.8 | 9.7 | 26.1 | |
| 1959 | 356 336 | 87 971 | 268 365 | 37.0 | 9.1 | 27.9 | |
| 1960 | 361 702 | 84 918 | 276 784 | 36.6 | 8.6 | 28.0 | |
| 1961 | 363 677 | 81 653 | 282 024 | 35.8 | 8.0 | 27.8 | |
| 1962 | 370 762 | 88 928 | 281 834 | 35.5 | 8.5 | 27.0 | |
| 1963 | 365 842 | 91 673 | 274 169 | 34.1 | 8.5 | 25.6 | |
| 1964 | 361 577 | 95 618 | 265 959 | 33.2 | 8.8 | 24.4 | |
| 1965 | 369 437 | 91 728 | 277 709 | 33.1 | 8.8 | 24.3 | |
| 1966 | 369 153 | 94 419 | 274 734 | 32.3 | 8.3 | 24.0 | |
| 1967 | 369 531 | 87 877 | 281 654 | 31.9 | 7.5 | 24.4 | |
| 1968 | 384 178 | 94 903 | 289 275 | 32.0 | 7.9 | 24.1 | |
| 1969 | 372 774 | 102 356 | 270 418 | 30.4 | 8.1 | 22.3 | |
| 1970 | 367 901 | 94 129 | 273 772 | 29.4 | 7.5 | 21.9 | |
| 1971 | 382 668 | 96 328 | 286 340 | 30.4 | 7.7 | 22.7 | |
| 1972 | 385 462 | 100 080 | 285 382 | 30.0 | 8.1 | 21.9 | |
| 1973 | 367 158 | 100 678 | 266 480 | 28.0 | 7.7 | 20.3 | |
| 1974 | 365 902 | 119 518 | 246 384 | 27.5 | 9.0 | 18.5 | |
| 1975 | 374 689 | 115 108 | 259 581 | 27.8 | 8.5 | 19.3 | |
| 1976 | 380 702 | 106 506 | 274 196 | 27.8 | 7.8 | 20.0 | |
| 1977 | 389 522 | 103 284 | 286 238 | 27.9 | 7.4 | 20.5 | |
| 1978 | 404 831 | 93 971 | 310 860 | 28.5 | 6.6 | 21.9 | |
| 1979 | 417 986 | 94 244 | 323 742 | 28.9 | 6.5 | 22.4 | |
| 1980 | 418 373 | 91 020 | 327 353 | 28.4 | 6.2 | 22.2 | |
| 1981 | 423 973 | 88 481 | 335 492 | 28.2 | 5.9 | 22.3 | |
| 1982 | 408 895 | 92 244 | 316 651 | 26.9 | 6.1 | 20.8 | |
| 1983 | 405 122 | 95 174 | 309 948 | 26.3 | 6.2 | 20.1 | |
| 1984 | 391 064 | 100 725 | 290 339 | 25.1 | 6.5 | 18.6 | |
| 1985 | 389 599 | 98 089 | 291 510 | 24.6 | 6.2 | 18.4 | |
| 1986 | 361 735 | 96 145 | 265 590 | 22.4 | 6.0 | 16.4 | |
| 1987 | 357 723 | 97 756 | 259 967 | 21.8 | 6.0 | 15.8 | |
| 1988 | 344 179 | 95 934 | 248 245 | 20.7 | 5.8 | 14.9 | |
| 1989 | 363 343 | 105 239 | 258 104 | 21.6 | 6.3 | 15.3 | |
| 1990 | 341 223 | 97 713 | 243 510 | 20.8 | 6.0 | 14.8 | |
| 1991 | 356 593 | 95 574 | 261 019 | 21.7 | 5.8 | 15.9 | |
| 1992 | 356 842 | 98 380 | 258 462 | 21.5 | 5.9 | 15.6 | |
| 1993 | 350 707 | 96 179 | 254 528 | 20.8 | 5.7 | 15.1 | |
| 1994 | 356 071 | 100 394 | 255 677 | 20.8 | 5.9 | 14.9 | |
| 1995 | 343 224 | 104 707 | 238 517 | 19.9 | 6.0 | 13.9 | |
| 1996 | 340 649 | 122 161 | 218 488 | 19.5 | 7.0 | 12.5 | |
| 1997 | 333 219 | 114 591 | 218 628 | 18.8 | 6.4 | 12.4 | |
| 1998 | 322 672 | 112 653 | 210 019 | 18.2 | 6.2 | 12.0 | |
| 1999 | 328 725 | 115 330 | 213 395 | 18.1 | 6.3 | 11.8 | |
| 2000 | 347 749 | 116 200 | 231 549 | 18.4 | 6.1 | 12.3 | |
| 2001 | 358 583 | 112 858 | 245 725 | 18.9 | 5.9 | 13.0 | |
| 2002 | 367 709 | 111 863 | 255 846 | 19.1 | 5.8 | 13.3 | |
| 2003 | 370 643 | 115 495 | 255 148 | 18.9 | 5.9 | 13.0 | |
| 2004 | 364 711 | 114 915 | 249 796 | 18.5 | 5.8 | 12.7 | |
| 2005 | 370 731 | 132 097 | 238 634 | 18.1 | 6.5 | 11.6 | |
| 2006 | 373 538 | 117 467 | 256 071 | 18.8 | 5.9 | 12.9 | |
| 2007 | 386 573 | 118 992 | 267 581 | 19.2 | 5.9 | 13.3 | |
| 2008 | 373 575 | 123 814 | 249 761 | 18.4 | 6.1 | 12.3 | |
| 2009 | 368 304 | 127 776 | 240 528 | 18.0 | 6.2 | 11.8 | |
| 2010 | 364 565 | 128 603 | 235 962 | 17.7 | 6.2 | 11.4 | |
| 2011 | 363 415 | 123 261 | 240 154 | 17.4 | 5.9 | 11.5 | |
| 2012 | 20,425,000 | 355 900 | 122 063 | 233 837 | 17.5 | 6.0 | 11.5 |
| 2013 | 20,585,000 | 365 792 | 127 124 | 238 668 | 17.9 | 6.2 | 11.7 |
| 2014 | 20,771,000 | 349 715 | 127 758 | 221 957 | 16.8 | 6.2 | 10.6 |
| 2015 | 20,966,000 | 334 821 | 131 634 | 203 187 | 16.0 | 6.3 | 9.7 |
| 2016 | 21,203,000 | 331 073 | 130 765 | 200 308 | 15.6 | 6.2 | 9.4 |
| 2017 | 21,444,000 | 326 052 | 139 822 | 186 230 | 15.2 | 6.5 | 8.7 |
| 2018 | 21,670,000 | 328 112 | 139 498 | 188 614 | 15.1 | 6.4 | 8.7 |
| 2019 | 21,803,000 | 319 010 | 146 053 | 172 957 | 14.6 | 6.7 | 7.9 |
Life expectancy[edit]
| Period | Life expectancy in Years |
Period | Life expectancy in Years |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 54.5 | 1985–1990 | 68.9 |
| 1955–1960 | 58.3 | 1990–1995 | 70.0 |
| 1960–1965 | 60.3 | 1995–2000 | 69.1 |
| 1965–1970 | 62.9 | 2000–2005 | 73.2 |
| 1970–1975 | 65.2 | 2005–2010 | 74.1 |
| 1975–1980 | 67.0 | 2010–2015 | 74.6 |
| 1980–1985 | 69.1 |
Source: UN World Population Prospects[38]
Population pyramid[edit]
Immigrant stock by source country[edit]
As of 2017, 40,018 foreign-born people lived in Sri Lanka per United Nations’ population division.[40]
| Country of birth | Population (2017) |
|---|---|
| 10,814 | |
| 5,107 | |
| 2,482 | |
| 1,755 | |
| 1,689 | |
| 1,417 | |
| 1,409 | |
| 1,193 | |
| 925 | |
| 849 | |
| 829 | |
| 741 | |
| 674 | |
| 613 | |
| 612 | |
| 611 | |
| 561 |
CIA World Factbook demographic statistics[edit]
Ethnicity in Sri Lanka (2012)[26]
The following demographic statistics are from the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated:[41]
- Population – 21,481,334 (July 2012 est.)[i]
- Age structure – 0–14 years: 23.9% (male 2,594,815/female 2,493,002); 15–64 years: 68% (male 7,089,307/female 7,418,123); 65 years and over:8.1% (male 803,172/female 926,372) (2010 est.)
- Median age – total: 31.1 years; male: 30.1 years; female: 32.2 years (2012 est.)
- Population growth rate – 0.913% (2012 est.)
- Birth rate – 17.04 births/1,000 population (2012 est.)
- Death rate – 5.96 deaths/1,000 population (July 2012 est.)
- Net migration rate – -1.95 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2012 est.)
- Urbanization – urban population: 14% of total population (2010); rate of urbanization: 1.1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
- Sex ratio – at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female; under 15 years: 1.04 male(s)/female; 15–64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female; 65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/female; total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2011 est.)
- Infant mortality rate – total: 9.47 deaths/1,000 live births; male: 10.44 deaths/1,000 live births; female: 8.45 deaths/1,000 live births
- Life expectancy at birth – total population: 75.94 years; male: 72.43 years; female: 79.59 years (2012 est.)
- Total fertility rate – 2.17 children born/woman (2012 est.)
- Health expenditures – 4% of GDP (2009)
- Physicians density – 0.492 physicians/1,000 population (2006)
- Hospital bed density – 3.1 beds/1,000 population (2004)
- HIV/AIDS – adult prevalence rate – less than 0.1% (2009 est.)
- HIV/AIDS – people living with HIV/AIDS – 2,800 (2009 est.)
- HIV/AIDS – deaths – fewer than 200 (2009 est.)
- Major infectious diseases – degree of risk: high; food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis A; vectorborne disease: dengue fever and chikungunya; water contact disease: leptospirosis; animal contact disease: rabies (2009)
- Nationality – noun: Sri Lankan(s);
adjective: Sri Lankan - Ethnic group – Sinhalese 73.8%; Sri Lankan Tamil 11.15%; Sri Lankan Moors 7.2%; Indian Tamil 4.6%; other 0.5%; unspecified 2.75% (2001 census provisional data)[j]
- Religion – Buddhism 70.19%; Hinduism 12.61%; Islam 9.71%; Christianity 7.45%; Other 0.05% (2012 [42] provisional data)
- Languages – Sinhala 74%; Tamil 25%; other 1%[k]
- Literacy – definition: age 15 and over can read and write; total population: 91.2%; male: 92.6%; female:90% (2010 census)