Akkadian language
| Akkadian | |
|---|---|
| 𒀝𒅗𒁺𒌑 akkadû |
|

Akkadian language inscription on the obelisk of Manishtushu
|
|
| Native to | Assyria and Babylon |
| Region | Mesopotamia |
| Era | c. 2500 – 600 BCE; academic or liturgical use until AD 100 |
|
|
| Sumero-Akkadian cuneiform | |
| Official status | |
|
Official language in
|
initially Akkad (central Mesopotamia); lingua franca of the Middle East and Egypt in the late Bronze and early Iron Ages. |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | akk |
| ISO 639-3 | akk |
| Glottolog | akka1240[1] |
Akkadian (/əˈkeɪdiən/ akkadû, 𒀝𒅗𒁺𒌑 ak-ka-du-u2; logogram: 𒌵𒆠 URIKI)[2][3] is an extinct East Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia (Akkad, Assyria, Isin, Larsa and Babylonia) from the third millennium BCE until its gradual replacement by Akkadian-influenced Old Aramaic among Mesopotamians by the 8th century BCE.
It is the earliest attested Semitic language.[4] It used the cuneiform script, which was originally used to write the unrelated, and also extinct, Sumerian (which is a language isolate). Akkadian is named after the city of Akkad, a major centre of Mesopotamian civilization during the Akkadian Empire (c. 2334–2154 BCE).
The mutual influence between Sumerian and Akkadian had led scholars to describe the languages as a Sprachbund.[5]
Akkadian proper names were first attested in Sumerian texts from around the mid 3rd-millennium BCE.[6] From about the 25th or 24th century BCE, texts fully written in Akkadian begin to appear. By the 10th century BCE, two variant forms of the language were in use in Assyria and Babylonia, known as Assyrian and Babylonian respectively. The bulk of preserved material is from this later period, corresponding to the Near Eastern Iron Age. In total, hundreds of thousands of texts and text fragments have been excavated, covering a vast textual tradition of mythological narrative, legal texts, scientific works, correspondence, political and military events, and many other examples.
Akkadian (in its Assyrian and Babylonian varieties) was the native language of the Mesopotamian empires (Akkadian Empire, Old Assyrian Empire, Babylonia, Middle Assyrian Empire) throughout the later Bronze Age, and Akkadian became the lingua franca of much of the Ancient Near East by the time of the Bronze Age collapse c 1150 BC. Its decline began in the Iron Age, during the Neo-Assyrian Empire, by about the 8th century BCE (Tiglath-Pileser III), in favour of Old Aramaic. By the Hellenistic period, the language was largely confined to scholars and priests working in temples in Assyria and Babylonia. The last known Akkadian cuneiform document dates from the 1st century AD.[7] Mandaic and Assyrian are two (Northwest Semitic) Neo-Aramaic languages that retain some Akkadian vocabulary and grammatical features.[8]
Akkadian is a fusional language with grammatical case; and like all Semitic languages, Akkadian uses the system of consonantal roots. The Kültepe texts, which were written in Old Assyrian, include Hittite loanwords and names, which constitute the oldest record of any Indo-European language.[9]
Classification
(circa 2200 BC)
Akkadian belongs with the other Semitic languages in the Near Eastern branch of the Afroasiatic languages, a family native to the Middle East, Arabian Peninsula, the Horn of Africa, parts of Anatolia, North Africa, Malta, Canary Islands and parts of West Africa (Hausa). Akkadian and its successor Aramaic, however, are only ever attested in Mesopotamia and the Near East.
Within the Near Eastern Semitic languages, Akkadian forms an East Semitic subgroup (with Eblaite). This group distinguishes itself from the Northwest and South Semitic languages by its subject–object–verb word order, while the other Semitic languages usually have either a verb–subject–object or subject–verb–object order.
Additionally Akkadian is the only Semitic language to use the prepositions ina and ana (locative case, English in/on/with, and dative-locative case, for/to, respectively). Other Semitic languages like Arabic and Aramaic have the prepositions bi/bə and li/lə (locative and dative, respectively). The origin of the Akkadian spatial prepositions is unknown.
In contrast to most other Semitic languages, Akkadian has only one non-sibilant fricative: ḫ [x]. Akkadian lost both the glottal and pharyngeal fricatives, which are characteristic of the other Semitic languages. Until the Old Babylonian period, the Akkadian sibilants were exclusively affricated.[3]
History and writing
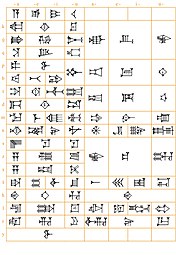
Writing
Cuneiform writing (Neoassyrian script)
(1 = Logogram (LG) “mix”/syllabogram (SG) ḫi,
2 = LG “moat”,
3 = SG aʾ,
4 = SG aḫ, eḫ, iḫ, uḫ,
5 = SG kam,
6 = SG im,
7 = SG bir)
Old Akkadian is preserved on clay tablets dating back to c. 2500 BC. It was written using cuneiform, a script adopted from the Sumerians using wedge-shaped symbols pressed in wet clay. As employed by Akkadian scribes, the adapted cuneiform script could represent either (a) Sumerian logograms (i.e., picture-based characters representing entire words), (b) Sumerian syllables, (c) Akkadian syllables, or (d) phonetic complements. However, in Akkadian the script practically became a fully fledged syllabic script, and the original logographic nature of cuneiform became secondary, though logograms for frequent words such as ‘god’ and ‘temple’ continued to be used. For this reason, the sign AN can on the one hand be a logogram for the word ilum (‘god’) and on the other signify the god Anu or even the syllable -an-. Additionally, this sign was used as a determinative for divine names.
Another peculiarity of Akkadian cuneiform is that many signs do not have a well-defined phonetic value. Certain signs, such as AḪ, do not distinguish between the different vowel qualities. Nor is there any coordination in the other direction; the syllable -ša-, for example, is rendered by the sign ŠA, but also by the sign NĪĜ. Both of these are often used for the same syllable in the same text.
Cuneiform was in many ways unsuited to Akkadian: among its flaws was its inability to represent important phonemes in Semitic, including a glottal stop, pharyngeals, and emphatic consonants. In addition, cuneiform was a syllabary writing system—i.e., a consonant plus vowel comprised one writing unit—frequently inappropriate for a Semitic language made up of triconsonantal roots (i.e., three consonants plus any vowels).
Development
Akkadian is divided into several varieties based on geography and historical period:[12]
- Old Akkadian, 2500–1950 BC
- Old Babylonian and Old Assyrian, 1950–1530 BC
- Middle Babylonian and Middle Assyrian, 1530–1000 BC
- Neo-Babylonian and Neo-Assyrian, 1000–600 BC
- Late Babylonian, 600 BC–100 AD
One of the earliest known Akkadian inscriptions was found on a bowl at Ur, addressed to the very early pre-Sargonic king Meskiagnunna of Ur (c. 2485–2450 BC) by his queen Gan-saman, who is thought to have been from Akkad.[13] The Akkadian Empire, established by Sargon of Akkad, introduced the Akkadian language (the “language of Akkad“) as a written language, adapting Sumerian cuneiform orthography for the purpose. During the Middle Bronze Age (Old Assyrian and Old Babylonian period), the language virtually displaced Sumerian, which is assumed to have been extinct as a living language by the 18th century BC.
Old Akkadian, which was used until the end of the 3rd millennium BC, differed from both Babylonian and Assyrian, and was displaced by these dialects. By the 21st century BC Babylonian and Assyrian, which were to become the primary dialects, were easily distinguishable. Old Babylonian, along with the closely related dialect Mariotic, is clearly more innovative than the Old Assyrian dialect and the more distantly related Eblaite language. For this reason, forms like lu-prus (‘I will decide’) were first encountered in Old Babylonian instead of the older la-prus. While generally more archaic, Assyrian developed certain innovations as well, such as the “Assyrian vowel harmony“. Eblaite was even more so, retaining a productive dual and a relative pronoun declined in case, number and gender. Both of these had already disappeared in Old Akkadian. Over 20,000 cuneiform tablets in Old Akkadian have been recovered from the Kültepe site in Anatolia. Most of the archaeological evidence is typical of Anatolia rather than of Assyria, but the use both of cuneiform and the dialect is the best indication of Assyrian presence.[14]
Old Babylonian was the language of king Hammurabi and his code, which is one of the oldest collections of laws in the world. (see Code of Ur-Nammu.) The Middle Babylonian (or Assyrian) period started in the 16th century BC. The division is marked by the Kassite invasion of Babylonia around 1550 BC. The Kassites, who reigned for 300 years, gave up their own language in favor of Akkadian, but they had little influence on the language. At its apogee, Middle Babylonian was the written language of diplomacy of the entire Ancient Near East, including Egypt. During this period, a large number of loan words were included in the language from Northwest Semitic languages and Hurrian; however, the use of these words was confined to the fringes of the Akkadian-speaking territory.
Middle Assyrian served as a lingua franca in much of the Ancient Near East of the Late Bronze Age (Amarna Period). During the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Assyrian began to turn into a chancellery language, being marginalized by Old Aramaic. Under the Achaemenids, Aramaic continued to prosper, but Assyrian continued its decline. The language’s final demise came about during the Hellenistic period when it was further marginalized by Koine Greek, even though Neo-Assyrian cuneiform remained in use in literary tradition well into Parthian times. The latest known text in cuneiform Babylonian is an astronomical almanac dated to 79/80 AD.[15] However, the latest cuneiform texts are almost entirely written in Sumerian logograms.[16]
Old Assyrian developed as well during the second millennium BC, but because it was a purely popular language — kings wrote in Babylonian — few long texts are preserved. From 1500 BC onwards, the language is termed Middle Assyrian.
During the first millennium BC, Akkadian progressively lost its status as a lingua franca. In the beginning, from around 1000 BC, Akkadian and Aramaic were of equal status, as can be seen in the number of copied texts: clay tablets were written in Akkadian, while scribes writing on papyrus and leather used Aramaic. From this period on, one speaks of Neo-Babylonian and Neo-Assyrian. Neo-Assyrian received an upswing in popularity in the 10th century BC when the Assyrian kingdom became a major power with the Neo-Assyrian Empire, but texts written ‘exclusively’ in Neo-Assyrian disappear within 10 years of Nineveh‘s destruction in 612 BC. The dominance of the Neo-Assyrian Empire under Tiglath-Pileser III over Aram-Damascus in the middle of the 8th century led to the establishment of Aramaic as a lingua franca[17] of the empire, rather than it being eclipsed by Akkadian.
After the end of the Mesopotamian kingdoms, which were conquered by the Persians, Akkadian (which existed solely in the form of Late Babylonian) disappeared as a popular language. However, the language was still used in its written form; and even after the Greek invasion under Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC, Akkadian was still a contender as a written language, but spoken Akkadian was likely extinct by this time, or at least rarely used. The last positively identified Akkadian text comes from the 1st century AD.[18]
Decipherment[edit]
The Akkadian language began to be rediscovered when Carsten Niebuhr in 1767 was able to make extensive copies of cuneiform texts and published them in Denmark. The deciphering of the texts started immediately, and bilinguals, in particular Old Persian-Akkadian bilinguals, were of great help. Since the texts contained several royal names, isolated signs could be identified, and were presented in 1802 by Georg Friedrich Grotefend. By this time it was already evident that Akkadian was a Semitic language, and the final breakthrough in deciphering the language came from Edward Hincks, Henry Rawlinson and Jules Oppert in the middle of the 19th century. The Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago recently completed a 21-volume dictionary of the Akkadian language, which is available commercially and online.[19]
Dialects
The following table summarises the dialects of Akkadian identified with certainty so far.
| Dialect | Location |
|---|---|
| Assyrian | Northern Mesopotamia |
| Babylonian | Central and Southern Mesopotamia |
| Mariotic | Central Euphrates (in and around the city of Mari) |
| Tell Beydar | Northern Syria (in and around Tell Beydar) |
Some researchers (such as W. Sommerfeld 2003) believe that the Old Akkadian variant used in the older texts is not an ancestor of the later Assyrian and Babylonian dialects, but rather a separate dialect that was replaced by these two dialects and which died out early.
Eblaite, formerly thought of as yet another Akkadian dialect, is now generally considered a separate East Semitic language.
Phonetics and phonology
Because Akkadian as a spoken language is extinct and no contemporary descriptions of the pronunciation are known, little can be said with certainty about the phonetics and phonology of Akkadian. Some conclusions can be made, however, due to the relationship to the other Semitic languages and variant spellings of Akkadian words.
Consonants
The following table gives the consonant sounds distinguished in the Akkadian use of cuneiform, with the presumed pronunciation in IPA transcription according to Huehnergard and Woods,[3] which most closely corresponds to recent reconstructions of Proto-Semitic phonology. The parenthesised symbol following is the transcription used in the literature, in the cases where that symbol is different from the phonetic symbol. This transcription has been suggested for all Semitic languages by the Deutsche Morgenländische Gesellschaft (DMG), and is therefore known as DMG-Umschrift.
| Labial | Dental/Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ||||
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t | k | ʔ ⟨ʾ⟩ | |
| voiced | b | d | ɡ | |||
| emphatic | tʼ ⟨ṭ⟩ | kʼ ⟨q⟩ | ||||
| Fricative | voiceless | s ~ ʃ ⟨š⟩ | x ⟨ḫ⟩ | |||
| voiced | ɣ ~ ʁ ⟨r⟩ | |||||
| Affricate | voiceless | t͡s ⟨s⟩ | ||||
| voiced | d͡z ⟨z⟩ | |||||
| emphatic | t͡s’ ⟨ṣ⟩ | |||||
| Approximant | l | j ⟨y⟩ | w | |||
Reconstruction
Akkadian emphatic consonants are typically reconstructed as ejectives, which are thought to be the oldest realization of emphatics across the Semitic languages.[22] One piece of evidence for this is that Akkadian shows a development known as Geers’ law, where one of two emphatic consonants dissimilates to the corresponding non-emphatic consonant. For the sibilants, traditionally /š/ has been held to be postalveolar [ʃ], and /s/, /z/, /ṣ/ analyzed as fricatives; but attested assimilations in Akkadian suggest otherwise.[3][23] For example, when the possessive suffix -šu is added to the root awat (‘word’), it is written awassu (‘his word’) even though šš would be expected. The most straightforward interpretation of this shift from tš to ss is that /s, ṣ/ form a pair of voiceless alveolar affricates [t͡s t͡sʼ], *š is a voiceless alveolar fricative [s], and *z is a voiced alveolar affricate or fricative [d͡z~z]. The assimilation is then [awat+su] > [awatt͡su]. In this vein, an alternative transcription of *š is *s̠, with the macron below indicating a soft (lenis) articulation in Semitic transcription. Other interpretations are possible, however. [ʃ] could have been assimilated to the preceding [t], yielding [ts], which would later have been simplified to [ss].
The phoneme /r/ has traditionally been interpreted as a trill but its pattern of alternation with /ḫ/ suggests it was a velar (or uvular) fricative. In the Hellenistic period, Akkadian /r/ was transcribed using the Greek ρ, indicating it was pronounced similarly as an alveolar trill (though Greeks may also have perceived a uvular trill as ρ).[3]
Descent from Proto-Semitic
Several Proto-Semitic phonemes are lost in Akkadian. The Proto-Semitic glottal stop *ʾ, as well as the fricatives *ʿ, *h, *ḥ are lost as consonants, either by sound change or orthographically, but they gave rise to the vowel quality e not exhibited in Proto-Semitic. The voiceless lateral fricatives (*ś, *ṣ́) merged with the sibilants as in Canaanite, leaving 19 consonantal phonemes. Old Akkadian preserved the /*ś/ phoneme longest but it eventually merged with /*š/, beginning in the Old Babylonian period.[3][24] The following table shows Proto-Semitic phonemes and their correspondences among Akkadian, Modern Standard Arabic and Tiberian Hebrew:
Inscription in Babylonian, in the Xerxes I inscription at Van, 5th century BCE
| Proto-Semitic | Akkadian | Arabic | Hebrew | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| *b | b | ب | b | ב | b |
| *d | d | د | d | ד | d |
| *g | g | ج | ǧ | ג | g |
| *p | p | ف | f | פ | p |
| *t | t | ت | t | ת | t |
| *k | k | ك | k | כ | k |
| *ʾ | (Ø)/ ʾ | ء | ʾ | א | ʾ |
| *ṭ | ṭ | ط | ṭ | ט | ṭ |
| *ḳ | q | ق | q | ק | q |
| *ḏ | z | ذ | ḏ | ז | z |
| *z | ز | z | |||
| *ṯ | š | ث | ṯ | שׁ | š |
| *š | س | s | |||
| *ś | ش | š | שׂ | ś | |
| *s | s | س | s | ס | s |
| *ṱ | ṣ | ظ | ẓ | צ | ṣ |
| *ṣ | ص | ṣ | |||
| *ṣ́ | ض | ḍ | |||
| *ġ | ḫ | غ | ġ | ע | ʿ [ʕ] |
| *ʿ | (e) [t2 1] | ع | ʿ [ʕ] | ||
| *ḫ | ḫ | خ | ḫ [x] | ח | ḥ |
| *ḥ | (e) [t2 1] | ح | ḥ [ħ] | ||
| *h | (Ø) | ه | h | ה | h |
| *m | m | م | m | מ | m |
| *n | n | ن | n | נ | n |
| *r | r | ر | r | ר | r |
| *l | l | ل | l | ל | l |
| *w | w | و | w | ו י |
w y |
| *y | y | ي | y [j] | י | y |
| Proto-Semitic | Akkadian | Arabic | Hebrew | ||
- ^ Jump up to:a b These are only distinguished from the Ø (zero) reflexes of /h/ and /ʾ/ by /e/-coloring the adjacent vowel *a, e.g. PS *ˈbaʿ(a)l-um (‘owner, lord’) → Akk. bēlu(m) (Dolgopolsky 1999, p. 35).
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Closed | i | u | |
| Mid | e | ||
| Open | a |
The existence of a back mid-vowel /o/ has been proposed, but the cuneiform writing gives no good proof for this.[25] There is limited contrast between different u-signs in lexical texts, but this scribal differentiation may reflect the superimposition of the Sumerian phonological system (for which an /o/ phoneme has also been proposed), rather than a separate phoneme in Akkadian.[26]
All consonants and vowels appear in long and short forms. Long consonants are represented in writing as double consonants, and long vowels are written with a macron (ā, ē, ī, ū). This distinction is phonemic, and is used in the grammar, for example iprusu (‘that he decided’) versus iprusū (‘they decided’).
Stress
The stress patterns of Akkadian are disputed, with some authors claiming that nothing is known of the topic. There are however certain points of reference, such as the rule of vowel syncope, and some forms in the cuneiform that might represent the stressing of certain vowels; however, attempts at identifying a rule for stress have so far been unsuccessful.
Huenergard (2005:3-4) claims that stress in Akkadian is completely predictable. In his syllable typology there are three syllable weights: light (V, CV); heavy (CVC, CV̄, CV̂), and superheavy (CV̂C). If the last syllable is superheavy, it is stressed, otherwise the rightmost heavy non-final syllable is stressed. If a word contains only light syllables, the first syllable is stressed.
A rule of Akkadian phonology is that certain short (and probably unstressed) vowels are dropped. The rule is that the last vowel of a succession of syllables that end in a short vowel is dropped, for example the declinational root of the verbal adjective of a root PRS is PaRiS-. Thus the masculine singular nominative is PaRS-um (< *PaRiS-um) but the feminine singular nominative is PaRiStum (< *PaRiS-at-um). Additionally there is a general tendency of syncope of short vowels in the later stages of Akkadian.
Grammar
Neo-Babylonian inscription of king Nebuchadnezzar II, 7th century BCE
Morphology
Consonantal root
Most roots of the Akkadian language consist of three consonants (called the radicals), but some roots are composed of four consonants (so-called quadriradicals). The radicals are occasionally represented in transcription in upper-case letters, for example PRS (to decide). Between and around these radicals various infixes, suffixes and prefixes, having word generating or grammatical functions, are inserted. The resulting consonant-vowel pattern differentiates the original meaning of the root. Also, the middle radical can be geminated, which is represented by a doubled consonant in transcription (and sometimes in the cuneiform writing itself).
The consonants ʔ, w, j and n are termed “weak radicals” and roots containing these radicals give rise to irregular forms.
Case, number and gender
Formally, Akkadian has three numbers (singular, dual and plural) and three cases (nominative, accusative and genitive). However, even in the earlier stages of the language, the dual number is vestigial, and its use is largely confined to natural pairs (eyes, ears, etc.), and adjectives are never found in the dual. In the dual and plural, the accusative and genitive are merged into a single oblique case.
Akkadian, unlike Arabic,has only “sound” plurals formed by means of a plural ending (i.e. no broken plurals formed by changing the word stem). As in all Semitic languages, some masculine nouns take the prototypically feminine plural ending (-āt).
The nouns šarrum (king) and šarratum (queen) and the adjective dannum (strong) will serve to illustrate the case system of Akkadian.
| Noun (masc.) | Noun (fem.) | Adjective (masc.) | Adjective (fem.) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative singular | šarr-um | šarr-at-um | dann-um | dann-at-um |
| Genitive singular | šarr-im | šarr-at-im | dann-im | dann-at-im |
| Accusative singular | šarr-am | šarr-at-am | dann-am | dann-at-am |
| Nominative dual | šarr-ān | šarr-at-ān | ||
| Oblique dual [t3 1] | šarr-īn | šarr-at-īn | ||
| Nominative plural | šarr-ū | šarr-āt-um | dann-ūt-um | dann-āt-um |
| Oblique plural | šarr-ī | šarr-āt-im | dann-ūt-im | dann-āt-im |
- ^ The oblique case includes the accusative and genitive.
As is clear from the above table, the adjective and noun endings differ only in the masculine plural. Certain nouns, primarily those referring to geography, can also form a locative ending in -um in the singular and the resulting forms serve as adverbials. These forms are generally not productive, but in the Neo-Babylonian the um-locative replaces several constructions with the preposition ina.
In the later stages of Akkadian the mimation (word-final -m) – along with nunation (dual final “-n”) – that occurred at the end of most case endings disappeared, except in the locative. Later, the nominative and accusative singular of masculine nouns collapsed to -u and in Neo-Babylonian most word-final short vowels were dropped. As a result, case differentiation disappeared from all forms except masculine plural nouns. However many texts continued the practice of writing the case endings (although often sporadically and incorrectly). As the most important contact language throughout this period was Aramaic, which itself lacks case distinctions, it is possible that Akkadian’s loss of cases was an areal as well as phonological phenomenon.
Noun states and nominal sentences
“Antiochus, King, Great King, King of multitudes, King of Babylon, King of countries”
As is also the case in other Semitic languages, Akkadian nouns may appear in a variety of “states” depending on their grammatical function in a sentence. The basic form of the noun is the status rectus (the governed state), which is the form as described above, complete with case endings. In addition to this, Akkadian has the status absolutus (the absolute state) and the status constructus (Construct state). The latter is found in all other Semitic languages, while the former appears only in Akkadian and some dialects of Aramaic.
The status absolutus is characterised by the loss of a noun’s case ending (e.g. awīl < awīlum, šar < šarrum). It is relatively uncommon, and is used chiefly to mark the predicate of a nominal sentence, in fixed adverbial expressions, and in expressions relating to measurements of length, weight, and the like.
(1) Awīl-um šū šarrāq
| Awīl-um | šū | šarrāq. | ||
| Man (Masculine, nominative) | he (3rd masc. personal pronoun) | thief (status absolutus) | ||
Translation: This man is a thief
(2) šarrum lā šanān
| šarr-um | lā | šanān. | ||
| King (Status rectus, nominative) | not (negative particle) | oppose (verbal infinitive, status absolutus) | ||
Translation: The king who cannot be rivaled
The status constructus is a great deal more common, and has a much wider range of applications. It is employed when a noun is followed by another noun in the genitive, a pronominal suffix, or a verbal clause in the subjunctive, and typically takes the shortest form of the noun which is phonetically possible. In general, this amounts to the loss of case endings with short vowels, with the exception of the genitive -i in nouns preceding a pronominal suffix, hence:
(3) māri-šu
| māri-šu |
| Son (status constructus) + his (3rd person singular possessive pronoun) |
Translation: His son, its (masculine) son
but
(4) mār šarr-im
| mār | šarr-im |
| Son (Status constructus) | king (genitive singular) |
Translation: The king’s son
There are numerous exceptions to this general rule, usually involving potential violations of the language’s phonological limitations. Most obviously, Akkadian does not tolerate word final consonant clusters, so nouns like kalbum (dog) and maḫrum (front) would have illegal construct state forms *kalb and *maḫr unless modified. In many of these instances, the first vowel of the word is simply repeated (e.g. kalab, maḫar). This rule, however, does not always hold true, especially in nouns where a short vowel has historically been elided (e.g. šaknum < *šakinum “governor”). In these cases, the lost vowel is restored in the construct state (so šaknum yields šakin).
(5) kalab belim
| kalab | bel-im |
| dog (Status constructus) | master (genitive singular) |
Translation: The master’s dog
(6) šakin ālim
| šakin | āl-im |
| Governor (Status constructus) | city (genitive singular) |
A genitive relation can also be expressed with the relative preposition ša, and the noun that the genitive phrase depends on appears in status rectus.
(7) salīmātum ša awīl Ešnunna
| salīmātum | ša | awīl | Ešnunna | ||
| Alliances (Status rectus, nominative) | which (relative particle) | man (status constructus) | Ešnunna (genitive, unmarked) | ||
Translation: The alliances of the Ruler of Ešnunna (literally “Alliances which man of Ešnunna (has)”)
The same preposition is also used to introduce true relative clauses, in which case the verb is placed in the subjunctive mood.
(7) awīl-um ša māt-am i-kšud-Ø-u
| Awīl-um | ša | māt-am | i-kšud-Ø-u | ||
| Man (Masculine, nominative) | that (relative pronoun) | land (singular, accusative) | 3rd person – conquer (preterite) – singular, masculine – subjunctive | ||
Translation: The man who conquered the land
Verbal morphology
Verb aspects
The Akkadian verb has six finite verb aspects (preterite, perfect, present, imperative, precative and vetitive) and three infinite forms (infinitive, participle and verbal adjective). The preterite is used for actions that are seen by the speaker as having occurred at a single point in time. The present is primarily imperfective in meaning and is used for concurrent and future actions as well as past actions with a temporal dimension. The final three finite forms are injunctive where the imperative and the precative together form a paradigm for positive commands and wishes, and the vetitive is used for negative wishes. Additionally the periphrastic prohibitive, formed by the present form of the verb and the negative adverb lā, is used to express negative commands. The infinitive of the Akkadian verb is a verbal noun, and in contrast to some other languages the Akkadian infinitive can be declined in case. The verbal adjective is an adjectival form and designates the state or the result of the action of the verb, and consequently the exact meaning of the verbal adjective is determined by the semantics of the verb itself. The participle, which can be active or passive, is another verbal adjective and its meaning is similar to the English gerund.
The following table shows the conjugation of the G-stem verbs derived from the root PRS (“to decide”) in the various verb aspects of Akkadian:
| Preterite | Perfect | Present | Imperative | stative | Infinitive | Participle (active) | Verbal adjective | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | aprus | aptaras | aparras | parsāku | parāsum | pārisum (masc.) pāristum (fem.) |
parsum (masc.) paristum (fem.) |
|
| 1st person plural | niprus | niptaras | niparras | parsānu | ||||
| 2nd person singular masc. | taprus | taptaras | taparras | purus | parsāta | |||
| 2nd person singular fem. | taprusī | taptarsī (< *taptarasī) | taparrasī | pursi | parsāti | |||
| 2nd person plural | taprusā | taptarsā | taparrasā | pursa | parsātunu (masc.) / parsātina(fem.) | |||
| 3rd person singular | iprus | iptaras | iparras | paris (masc.) /parsat (fem.) | ||||
| 3rd person plural masc. | iprusū | iptarsū (< *iptarasū) | iparrasū | parsū | ||||
| 3rd person plural fem. | iprusā | iptarsā(< *iptarasā) | iparrasā | parsā |
The table below shows the different affixes attached to the preterite aspect of the verb root PRS “to decide”; and as can be seen, the grammatical genders differ only in the second person singular and third person plural.
| G-Stem | D-Stem | Š-Stem | N-Stem | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st person singular | a-prus-Ø | u-parris-Ø | u-šapris-Ø | a-pparis-Ø |
| 1st person plural | ni-prus-Ø | nu-parris-Ø | nu-šapris-Ø | ni-pparis-Ø |
| 2nd person singular masc. | ta-prus-Ø | tu-parris-Ø | tu-šapris-Ø | ta-pparis-Ø |
| 2nd person singular fem. | ta-prus-ī | tu-parris-ī | tu-šapris-ī | ta-ppars-ī |
| 2nd person plural | ta-prus-ā | tu-parris-ā | tu-šapris-ā | ta-ppars-ā |
| 3rd person singular | i-prus-Ø | u-parris-Ø | u-šapris-Ø | i-pparis-Ø |
| 3rd person plural masc. | i-prus-ū | u-parris-ū | u-šapris-ū | i-ppars-ū |
| 3rd person plural fem. | i-prus-ā | u-parris-ā | u-šapris-ā | i-ppars-ā |
Verb moods
Akkadian verbs have 3 moods:
- Indicative, used in independent clauses, is unmarked.
- Subjunctive, used in dependent clauses. The subjunctive is marked in forms which do not end in a vowel by the suffix -u (compare Arabic and Ugaritic subjunctives), but is otherwise unmarked. In the later stages of most dialects, the subjunctive is indistinct, as short final vowels were mostly lost
- Venitive or allative. The venitive is not a mood in the strictest sense, being a development of the 1st person dative pronominal suffix -am/-m/-nim. With verbs of motion, it often indicates motion towards an object or person (e.g. illik, “he went” vs. illikam, “he came”). However, this pattern is not consistent, even in earlier stages of the language, and its use often appears to serve a stylistic rather than morphological or lexical function.
The following table demonstrates the verb moods of verbs derived from the root PRS (“to decide”,”to separate”):
| Preterite.[t4 1] | Stative.[t4 1] | |
|---|---|---|
| Indicative | iprus | paris |
| Subjunctive | iprusu | parsu |
| Venitive | iprusam | parsam |
- ^ Jump up to:a b Both verbs are for the 3rd person masculine singular.
Verb patterns
Akkadian verbs have thirteen separate derived stems formed on each root. The basic, underived, stem is the G-stem (from the German Grundstamm, meaning “basic stem”). Causative or intensive forms are formed with the doubled D-stem, and it gets its name from the doubled-middle radical that is characteristic of this form. The doubled middle radical is also characteristic of the present, but the forms of the D-stem use the secondary conjugational affixes, so a D-form will never be identical to a form in a different stem. The Š-stem is formed by adding a prefix š-, and these forms are mostly causatives. Finally, the passive forms of the verb are in the N-stem, formed by adding a n- prefix. However the n- element is assimilated to a following consonant, so the original /n/ is only visible in a few forms.
Furthermore, reflexive and iterative verbal stems can be derived from each of the basic stems. The reflexive stem is formed with an infix -ta, and the derived stems are therefore called Gt, Dt, Št and Nt, and the preterite forms of the Xt-stem are identical to the perfects of the X-stem. Iteratives are formed with the infix -tan-, giving the Gtn, Dtn, Štn and Ntn. Because of the assimilation of n, the /n/ is only seen in the present forms, and the Xtn preterite is identical to the Xt durative.
The final stem is the ŠD-stem, a form mostly attested only in poetic texts, and whose meaning is usually identical to either the Š-stem or the D-stem of the same verb. It is formed with the Š prefix (like the Š-stem) in addition to a doubled-middle radical (like the D-stem).
An alternative to this naming system is a numerical system. The basic stems are numbered using Roman numerals so that G, D, Š and N become I, II, III and IV, respectively, and the infixes are numbered using Arabic numerals; 1 for the forms without an infix, 2 for the Xt, and 3 for the Xtn. The two numbers are separated using a solidus. As an example, the Štn-stem is called III/3. The most important user of this system is the Chicago Assyrian Dictionary.
There is mandatory congruence between the subject of the sentence and the verb, and this is expressed by prefixes and suffixes. There are two different sets of affixes, a primary set used for the forms of the G and N-stems, and a secondary set for the D and Š-stems.
The stems, their nomenclature and examples of the third-person masculine singular stative of the verb parāsum (root PRS: ‘to decide, distinguish, separate’) is shown below:
| # | Stem | Verb | Description | Correspondence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I.1 | G | PaRiS | the simple stem, used for transitive and intransitive verbs | Arabic stem I (fa‘ala) and Hebrew pa’al |
| II.1 | D | PuRRuS | gemination of the second radical, indicating the intensive | Arabic stem II (fa‘‘ala) and Hebrew pi‘el |
| III.1 | Š | šuPRuS | š-preformative, indicating the causative | Arabic stem IV (’af‘ala) and Hebrew hiph‘il |
| IV.1 | N | naPRuS | n-preformative, indicating the reflexive/passive | Arabic stem VII (infa‘ala) and Hebrew niph‘al |
| I.2 | Gt | PitRuS | simple stem with t-infix after first radical, indicating reciprocal or reflexive | Arabic stem VIII (ifta‘ala) and Aramaic ’ithpe‘al (tG) |
| II.2 | Dt | PutaRRuS | doubled second radical preceded by infixed t, indicating intensive reflexive | Arabic stem V (tafa‘‘ala) and Hebrew hithpa‘el (tD) |
| III.2 | Št | šutaPRuS | š-preformative with t-infix, indicating reflexive causative | Arabic stem X (istaf‘ala) and Aramaic ’ittaph‘al (tC) |
| IV.2 | Nt | itaPRuS | n-preformative with a t-infix preceding the first radical, indicating reflexive passive | |
| I.3 | Gtn | PitaRRuS | ||
| II.3 | Dtn | PutaRRuS | doubled second radical preceded by tan-infix | |
| III.3 | Štn | šutaPRuS | š-preformative with tan-infix | |
| IV.3 | Ntn | itaPRuS | n-preformative with tan-infix | |
| ŠD | šuPuRRuS | š-preformative with doubled second radical |
Stative
A very often appearing form which can be formed by nouns, adjectives as well as by verbal adjectives is the stative. Nominal predicatives occur in the status absolutus and correspond to the verb “to be” in English. The stative in Akkadian corresponds to the Egyptian pseudo-participle. The following table contains an example of using the noun šarrum (king), the adjective rapšum (wide) and the verbal adjective parsum (decided).
| šarrum | rapšum | parsum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Person singular | šarr-āku | rapš-āku | pars-āku |
| 1st Person plural | šarr-ānu | rapš-ānu | pars-ānu |
| 2nd Person singular masc. | šarr-āta | rapš-āta | pars-āta |
| 2nd Person singular fem. | šarr-āti | rapš-āti | pars-āti |
| 2nd Person plural masc. | šarr-ātunu | rapš-ātunu | pars-ātunu |
| 2nd Person plural fem. | šarr-ātina | rapš-ātina | pars-ātina |
| 3rd Person singular masc. | šar-Ø | rapaš-Ø | paris-Ø |
| 3rd Person singular fem. | šarr-at | rapš-at | pars-at |
| 3rd Person plural masc. | šarr-ū | rapš-ū | pars-ū |
| 3rd Person plural fem. | šarr-ā | rapš-ā | pars-ā |
Thus, the stative in Akkadian is used to convert simple stems into effective sentences, so that the form šarr-āta is equivalent to: “you were king”, “you are king” and “you will be king”. Hence, the stative is independent of time forms.
Derivation
Beside the already explained possibility of derivation of different verb stems, Akkadian has numerous nominal formations derived from verb roots. A very frequently encountered form is the maPRaS form. It can express the location of an event, the person performing the act and many other meanings. If one of the root consonants is labial (p, b, m), the prefix becomes na- (maPRaS > naPRaS). Examples for this are: maškanum (place, location) from ŠKN (set, place, put), mašraḫum (splendour) from ŠRḪ (be splendid), maṣṣarum (guards) from NṢR (guard), napḫarum (sum) from PḪR (summarize).
A very similar formation is the maPRaSt form. The noun derived from this nominal formation is grammatically feminine. The same rules as for the maPRaS form apply, for example maškattum (deposit) from ŠKN (set, place, put), narkabtum (carriage) from RKB (ride, drive, mount).
The suffix – ūt is used to derive abstract nouns. The nouns which are formed with this suffix are grammatically feminine. The suffix can be attached to nouns, adjectives and verbs, e.g. abūtum (paternity) from abum (father), rabutum (size) from rabum (large), waṣūtum (leaving) from WṢY (leave).
Also derivatives of verbs from nouns, adjectives and numerals are numerous. For the most part, a D-stem is derived from the root of the noun or adjective. The derived verb then has the meaning of “make X do something” or “becoming X”, for example: duššûm (let sprout) from dišu (grass), šullušum (to do something for the third time ) from šalāš (three).
Pronouns
Personal pronouns
Independent personal pronouns
Independent personal pronouns in Akkadian are as follows:
| Nominative | Oblique | Dative | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| 1st | anāku “I” | nīnu “we” | yāti | niāti | yāšim | niāšim | |
| 2nd | masculine | atta “you” | attunu “you” | kāti (kāta) | kunūti | kāšim | kunūšim |
| feminine | atti “you” | attina “you” | kāti | kināti | kāšim | kināšim | |
| 3rd | masculine | šū “he” | šunu “they” | šātilu (šātilu) | šunūti | šuāšim (šāšim) | šunūšim |
| feminine | šī “she” | šina “they” | šiāti (šuāti;šāti) | šināti | šiāšim (šāšim, šāšim) | šināšim | |
Suffixed (or enclitic) pronouns
Suffixed (or enclitic) pronouns (mainly denoting the genitive, accusative and dative) are as follows:
| Genitive | Accusative | Dative | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| 1st | -i, -ya [t5 1] | -ni | -ni | -niāti | -am/-nim | -niāšim | |
| 2nd | masculine | -ka | -kunu | -ka | -kunūti | -kum | -kunūšim |
| feminine | -ki | -kina | -ki | -kināti | -kim | -kināšim | |
| 3rd | masculine | -šū | -šunu | -šū | -šunūti | -šum | -šunūšim |
| feminine | -ša | -šina | -ši | -šināti | -šim | -šināšim | |
- ^ -ni is used for the nominative, i.e. following a verb denoting the subject.
Demonstrative pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns in Akkadian differ from the Western Semitic variety. The following table shows the Akkadian demonstrative pronouns according to near and far deixis:
| Deixis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Proximal | Distal | |
| Masc. singular | annū “this” | ullū “that” |
| Fem. Singular | annītu “this” | ullītu “that” |
| Masc. plural | annūtu “these” | ullūtu “those” |
| Fem. plural | annātu “these” | ullātu “those” |
Relative pronouns
Relative pronouns in Akkadian are shown in the following table:
| Nominative | Accusative | Genitive | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Masc. singular | šu | ša | ši |
| Fem. Singular | šāt | šāti | |
| Dual | šā | ||
| Masc. plural | šūt | ||
| Fem. plural | šāt | ||
Unlike plural relative pronouns, singular relative pronouns in Akkadian exhibit full declension for case. However, only the form ša (originally accusative masculine singular) survived, while the other forms disappeared in time.
Interrogative pronouns
The following table shows the Interrogative pronouns used in Akkadian:
| Akkadian | English |
|---|---|
| mannu | who? |
| mīnū | what? |
| ayyu | which? |
Prepositions
Akkadian has prepositions which consist mainly of only one word. For example: ina (in, on, out, through, under), ana (to, for, after, approximately), adi (to), aššu (because of), eli (up, over), ištu/ultu (of, since), mala (in accordance with), itti (also, with). There are, however, some compound prepositions which are combined with ina and ana (e.g. ina maḫar (forwards), ina balu (without), ana ṣēr (up to), ana maḫar (forwards). Regardless of the complexity of the preposition, the following noun is always in the genitive case.
Examples: ina bītim (in the house, from the house), ana dummuqim (to do good), itti šarrim (with the king), ana ṣēr mārīšu (up to his son).
Numerals
Since numerals are written mostly as a number sign in the cuneiform script, the transliteration of many numerals is not well ascertained yet. Along with the counted noun, the cardinal numerals are in the status absolutus. Because other cases are very rare, the forms of the status rectus are known only by isolated numerals. The numerals 1 and 2 as well as 21–29, 31–39, 41–49 correspond with the counted in the grammatical gender, while the numerals 3–20, 30, 40 and 50 are characterized by polarity of gender, i.e. if the counted noun is masculine, the numeral would be feminine and vice versa. This polarity is typical of the Semitic languages and appears also in classical Arabic for example. The numerals 60, 100 and 1000 do not change according to the gender of the counted noun. Counted nouns more than two appear in the plural form. However, body parts which occur in pairs appear in the dual form in Akkadian. e.g. šepum (foot) becomes šepān (two feet).
The ordinals are formed (with a few exceptions) by adding a case ending to the nominal form PaRuS (the P, R and S. must be substituted with the suitable consonants of the numeral). It is noted, however, that in the case of the numeral “one”, the ordinal (masculine) and the cardinal number are the same. A metathesis occurs in the numeral “four”.
| # | Cardinal | Congruence | Ordinal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (masculine) | (feminine) | (Gender agreement of the cardinal numeral) | (masculine) | (feminine) | |||
| (absolute) | (free) | (absolute) | (free) | ||||
| 1 | ištēn | (ištēnum) | išteat, ištēt | (ištētum) | Congruent (no gender polarity) | pānûm maḫrûm (ištīʾum) ištēn |
pānītum maḫrītum (ištītum) išteat |
| 2 | šinā | — | šittā | — | Congruent | šanûm | šanītum |
| 3 | šalāšat | šalāštum | šalāš | šalāšum | Gender polarity | šalšum | šaluštum |
| 4 | erbet(ti) | erbettum | erbe, erba | erbûm | Gender polarity | rebûm | rebūtum |
| 5 | ḫamšat | ḫamištum | ḫamiš | ḫamšum | Gender polarity | ḫamšum | ḫamuštum |
| 6 | šeššet | šedištum | šediš? | šeššum | Gender polarity | šeššum | šeduštum |
| 7 | sebet(ti) | sebettum | sebe | sebûm | Gender polarity | sebûm | sebūtum |
| 8 | samānat | samāntum | samāne | samānûm | Gender polarity | samnum | samuntum |
| 9 | tišīt | tišītum | tiše | tišûm | Gender polarity | tešûm | tešūtum |
| 10 | eš(e)ret | ešertum | ešer | eš(e)rum | Gender polarity | ešrum | ešurtum |
| 11 | ištēššeret | ištēššer | Gender polarity | ištēššerûm | ištēššerītum | ||
| 12 | šinšeret | šinšer | Gender polarity | šinšerûm | šinšerītum | ||
| 13 | šalāššeret | šalāššer | Gender polarity | šalāššerûm | šalāššerītum | ||
| 14 | erbēšeret | erbēšer | Gender polarity | erbēšerûm | erbēšerītum | ||
| 15 | ḫamiššeret | ḫamiššer | Gender polarity | ḫamiššerûm | ḫamiššerītum | ||
| 16 | šeššeret? | šeššer? | Gender polarity | šeššerûm? | šeššerītum? | ||
| 17 | sebēšeret | sebēšer | Gender polarity | sebēšerûm | sebēšerītum | ||
| 18 | samāššeret | samāššer | Gender polarity | samāššerûm | samāššerītum | ||
| 19 | tišēšeret | tišēšer | Gender polarity | tišēšerûm | tišēšerītum | ||
| 20 | ešrā | No gender distinction | ešrûm | ešrītum? | |||
| 30 | šalāšā | No gender distinction | (as with 20?) | ||||
| 40 | erbeā, erbâ | No gender distinction | (as with 20?) | ||||
| 50 | ḫamšā | No gender distinction | (as with 20?) | ||||
| 60 | absolute šūš(i), free šūšum | No gender distinction | (as with 20?) | ||||
| 100 | absolute sg. meat, pl. meât[32] (free meatum) | No gender distinction | (as with 20?) | ||||
| 600 | absolute nēr, free nērum | No gender distinction | (as with 20?) | ||||
| 1000 | absolute līm(i), free līmum | No gender distinction | (as with 20?) | ||||
| 3600 | absolute šār, free šārum | No gender distinction | (as with 20?) | ||||
Examples: erbē aššātum (four wives) (masculine numeral), meat ālānū (100 towns).
Syntax
Nominal phrases
Adjectives, relative clauses and appositions follow the noun. While numerals precede the counted noun. In the following table the nominal phrase erbēt šarrū dannūtum ša ālam īpušū abūya ‘the four strong kings who built the city are my fathers’ is analyzed:
| Word | Meaning | Analysis | Part of the nominal phrase |
|---|---|---|---|
| erbēt | four | feminine (gender polarity) | Numeral |
| šarr-ū | king | nominative plural | Noun (Subject) |
| dann-ūtum | strong | nominative masculine plural | Adjective |
| ša | which | relative pronoun | Relative clause |
| āl-am | city | accusative singular | |
| īpuš-ū | built | 3rd person masculine plural | |
| ab-ū-ya | my fathers | masculine plural + possessive pronoun | Apposition |
Sentence syntax
Akkadian sentence order was Subject+Object+Verb (SOV), which sets it apart from most other ancient Semitic languages such as Arabic and Biblical Hebrew, which typically have a verb–subject–object (VSO) word order. (Modern South Semitic languages in Ethiopia also have SOV order, but these developed within historical times from the classical verb–subject–object (VSO) language Ge’ez.) It has been hypothesized that this word order was a result of influence from the Sumerian language, which was also SOV. There is evidence that native speakers of both languages were in intimate language contact, forming a single society for at least 500 years, so it is entirely likely that a sprachbund could have formed.[33] Further evidence of an original VSO or SVO ordering can be found in the fact that direct and indirect object pronouns are suffixed to the verb. Word order seems to have shifted to SVO/VSO late in the 1st millennium BC to the 1st millennium AD, possibly under the influence of Aramaic.
Vocabulary
The Akkadian vocabulary is mostly of Semitic origin. Although classified as ‘East Semitic‘, many elements of its basic vocabulary find no evident parallels in related Semitic languages. For example: māru ‘son’ (Semitic *bn), qātu ‘hand’ (Semitic *yd), šēpu ‘foot’ (Semitic *rgl), qabû ‘say’ (Semitic *qwl), izuzzu ‘stand’ (Semitic *qwm), ana ‘to, for’ (Semitic *li).
Due to extensive contact with Sumerian and Aramaic, the Akkadian vocabulary contains many loan words from these languages. Aramaic loan words, however, were limited to the 1st centuries of the 1st millennium BC and primarily in the north and middle parts of Mesopotamia, whereas Sumerian loan words were spread in the whole linguistic area. Beside the previous languages, some nouns were borrowed from Hurrian, Kassite, Ugaritic and other ancient languages. Since Sumerian and Hurrian, two non-Semitic languages, differ from Akkadian in word structure, only nouns and some adjectives (not many verbs) were borrowed from these languages. However, some verbs were borrowed (along with many nouns) from Aramaic and Ugaritic, both of which are Semitic languages.
The following table contains examples of loan words in Akkadian:
| Akkadian | Meaning | Source | Word in the language of origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| dû | hill | Sumerian | du |
| erēqu | flee | Aramaic | ʿRQ (root) |
| gadalû | dressed in linen | Sumerian | gada lá |
| isinnu | firmly | Sumerian | ezen |
| kasulatḫu | a device of copper | Hurrian | kasulatḫ- |
| kisallu | court | Sumerian | kisal |
| laqāḫu | take | Ugaritic | LQḤ(root) |
| paraššannu | part of horse riding gear | Hurrian | paraššann- |
| purkullu | stone cutter | Sumerian | bur-gul |
| qaṭālu | kill | Aramaic | QṬL (root) |
| uriḫullu | conventional penalty | Hurrian | uriḫull- |
Akkadian was also a source of borrowing to other languages, above all Sumerian. Some examples are: Sumerian da-ri (‘lastingly’, from Akkadian dāru), Sumerian ra gaba (‘riders, messenger’, from Akkadian rākibu).
Sample text
The following is the 7th section of the Hammurabi law code, written in the mid-18th century BC:
lū
or
alp-am
cattle/oxen-acc
lū
or
immer-am
sheep-acc
lū
or
imēr-am
donkey-acc
ū
and
lū
or
mimma šumšu
something
ina
from
qāt
hand-const
mār
son-const
awīl-im
man-gen
ū
and
lū
or
warad
slave-const
awīl-im
man-gen
balum
without
šīb-ī
witnesses-gen
u
and
Translation:
- If a man has bought silver or gold, a male or a female slave,
an ox, a sheep, or a donkey—or anything for that matter—
from another man or from another man’s slave without witnesses or contract,
or if he accepted something for safekeeping without same,
then this man is a thief and hence to be killed.
Akkadian literature
- Atrahasis Epic (early 2nd millennium BC)
- Enûma Elish (c. 18th century BC)
- Amarna letters (14th century BC)
- Epic of Gilgamesh (Sin-liqe-unninni‘, Standard Babylonian version, 13th to 11th century BC)
- Ludlul Bel Nemeqi











0 thoughts on - Akkadian language
He was dressed in a silk coat,madeat Paris for his former master,ラブドール 最新